Leadership Transformation in the GCC: CHRO Insights on Shaping the Future
Leadership Transformation Isn’t Optional — It’s Survival
What happens when cost centers start becoming innovation hubs? When your “support team” begins leading global digital strategy? That’s the story of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) today.
GCCs are no longer back-end operations units- they are emerging as value creators, growth accelerators, and centers of leadership innovation. But while their role has evolved, many leadership styles within them have not. And that’s the bottleneck.
“You can’t power the future with a leadership model built for the past“.
This is where the CHRO must step in, not just as an HR function head but as a transformation architect. One who doesn’t merely manage talent but champions transforming leadership re-engineering mindsets to drive performance, agility, and innovation.
GCCs: From Cost Centers to Competitive Differentiators
The scale and sophistication of GCCs are growing rapidly. India, for instance, now houses over 1,580 GCCs employing more than 1.66 million professionals (NASSCOM, 2024). McKinsey observes the “10/30/50 approach”: 10% of enterprise leaders, 30% of global talent, and 50% of new-age skills now sit in GCCs- signaling their shift from support arms to innovation powerhouses.
This evolution demands a mastery of leadership skills—shifting focus from managing processes to managing outcomes, from task execution to strategic thinking, and from local efficiencies to global collaboration.
Leadership- more than technology- is the defining factor in this transformation.
Why Is Mindset Central to Modern Leadership Transformation?
Most organizations invest in tools and processes when they want transformation. But the most underutilized lever of change is also the most powerful: mindset.
GCC leadership often lags in this area. Built in traditional operational models, leaders tend to exhibit behaviors that are risk-averse, delivery-focused, and hierarchical. This doesn’t fit today’s environment that thrives on innovation, agility, and digital thinking.
A 2024 Deloitte Human Capital Trends report reveals that only 21% of GCC leaders feel prepared to lead in a digital-first, innovation-driven world
CHROs must be deliberate in shifting these deep-seated beliefs and behaviors, and that starts with reimagining how leadership is defined, developed, and deployed in the GCC context.
Top 5 CHRO Strategies to Transform Leadership in GCCs
Leadership transformation in GCCs requires deliberate, multidimensional interventions. Here’s a deeper dive into five strategic levers CHROs must pull to lead this change effectively.

1. Leadership Development That Mirrors Business Transformation
The problem: Most leadership development programs within GCCs are standardized, generic, and often imported from global HQs without contextual relevance. These programs fail to address the unique blend of operational, cultural, and innovation demands that GCC leaders face.
CHRO solution: Redesign leadership development to mirror real-time enterprise goals. Leaders must experience challenges that are ambiguous, complex, and cross-functional, just like the world they operate in.
Key components:
- Simulation-based assessments: Use real-life case studies from within the business to evaluate decision-making under pressure. These go beyond theory and test practical leadership acumen.
- Leadership labs: Assign business transformation problems to emerging leaders and give them autonomy, budget, and a timeline to solve them, like internal start-ups.
- Reverse mentoring: Pair digital-native Gen Z employees with senior leaders. This not only upskills leaders on tech but also fosters humility, openness, and modern communication practices.
- Shadow boards: Allow high-potential leaders to participate in executive decision-making processes to build their strategic thinking muscle.
End goal: Leaders don’t just learn- they transform how they think, lead, and solve.
2. Break the “Order-Taker” Culture, Enable Strategic Thinking
The problem: Many GCC leaders still operate in a “tell me what to do” culture. They focus on executing HQ directives instead of questioning, innovating, or suggesting strategic improvements. This restricts the GCC’s potential to lead value creation.
CHRO solution: Empower leaders to own strategy, not just execution. This involves fostering a mindset shift from servitude to stewardship.
How to implement:
- Training on business acumen: Leaders should be trained to understand enterprise-wide priorities, customer needs, market dynamics, and digital disruption.
- Freedom to fail: Build systems where intelligent failure is seen as a learning process, not a career risk.
- Reimagined KPIs: Move beyond service-level agreements and embed innovation metrics like “value delivered,” “problem-solving impact,” or “enterprise enablement score.”
- Innovation charters: Give each leader a mandate to drive one innovation initiative per quarter, no matter how small.
End goal: Leaders begin to act like entrepreneurs inside the enterprise—thinking bigger, faster, and beyond boundaries.
3. Power Transformation with People Analytics
The problem: Leadership identification and growth are often subjective. Promotions are based on tenure, visibility, or “who you know,” rather than data-backed potential. This blocks real talent from emerging.
CHRO solution: Use people analytics to make leadership transformation measurable, personalized, and predictive.
Tactics:
- 360° feedback analytics: Aggregate data from peers, reports, and managers to identify leadership behaviors that enable or derail team success.
- Leadership potential dashboards: Use predictive analytics to map future-ready traits such as resilience, curiosity, collaboration, and digital fluency.
- Attrition risk tracking: Identify where toxic leadership styles may be contributing to burnout or exit risks and intervene with targeted coaching.
- Customized development journeys: Tailor L&D modules to address the specific behavior or mindset gaps in each leader using data insights.
Example: A GCC in the healthcare tech sector used behavioral analytics to identify that 65% of its mid-level leaders struggled with ambiguity. They rolled out a “Leading in Uncertainty” track, resulting in better decision-making speed during project pivots.
End goal: Talent decisions are no longer based on intuition- they’re based on intelligent, predictive, and personalized data.
4. Design Inclusive, Future-Ready Leadership Archetypes
The problem: Many existing leadership models are still built on outdated ideals- assertiveness, dominance, and output over empathy, inclusion, and long-term impact. This makes leadership homogeneous and limits innovation.
CHRO solution: Build inclusive leadership archetypes rooted in modern behaviors- collaboration, adaptability, authenticity, and empathy. These models must reflect the diverse, global, and hybrid nature of today’s GCCs.
Steps to drive inclusivity:
- Inclusive behavior indicators: Add tangible inclusion metrics to leadership evaluations. For example, “Mentored 2+ team members from diverse backgrounds,” or “Created an environment of psychological safety.”
- Sponsorship over mentorship: Push senior leaders to sponsor high-potential talent from underrepresented groups- actively creating opportunities, not just advice.
- Bias interrupters in decision-making: Train leaders to recognize and override bias during hiring, promotions, and team building.
- Leadership diversity dashboards: Make DEI progress visible across levels. Include metrics on representation, engagement, and advancement.
Some advanced GCCs are now using AI-based sentiment analysis tools to assess inclusion in everyday communication- emails, meetings, and feedback sessions.
End goal: Leaders become magnets for diverse talent and create spaces where all voices are heard, valued, and leveraged.
5. Redefine Leadership Success Metrics
The problem: Too often, leadership success is measured by outdated metrics: output volume, team size, budget managed, or on-time delivery. These miss the essence of transformational leadership.
CHRO solution: Redefine leadership KPIs to align with enterprise innovation, human impact, and future readiness.
Modern leadership metrics may include:
- Innovation velocity: Number of new ideas initiated, tested, and implemented by the leader’s team
- Psychological safety score: Derived from team feedback tools like CultureAmp or Glint
- Cross-team collaboration index: Measuring effectiveness in leading across boundaries and silos
- Engagement uplift post-transition: Comparing team engagement scores before and after leadership change
- Digital quotient score (DQ): A composite measure of tech fluency, adoption rate of digital tools, and enablement of digital transformation initiatives
A US-based retail GCC shifted from individual performance ratings to team-based leadership effectiveness ratings, directly linked to team innovation output and engagement.
End goal: Leadership success becomes about what value you create, not what title you hold.
The CHRO’s Role: From HR Head to Strategic Co-Pilot
The CHRO is no longer responsible just for culture fit- they are responsible for culture shift.
This includes:
- Leading organizational design for agility
- Creating leadership feedback loops across levels
- Building transformation KPIs into scorecards
- Sitting at the table where enterprise change is discussed- not as an observer, but as a driver
When CHROs lead mindset transformation at the top, the ripple effect is enterprise-wide.
Case in Point: Leadership Transformation in Action
A leading European banking GCC based in Bangalore recently transformed its leadership layer through a CHRO-led initiative called “Leadershift.” The program combined reverse mentoring, agile team rotations, leadership “lab” projects, and analytics-backed coaching.
Results in 12 months:
- 37% increase in employee trust in leadership
- 21% faster cycle time for new digital product launches
- 2x increase in internal mobility across teams
This proves that leadership transformation is not theoretical, it delivers measurable ROI.
The Road Ahead: Building Leadership Resilience in GCCs
The future is not going to be stable- it will be volatile, complex, and boundaryless. Leadership models need to reflect that.
By 2027, over 60% of GCCs will own end-to-end digital product portfolios, requiring leaders who can collaborate across time zones, cultures, and technologies (Bain & Company, GCC Outlook 2024).
This means that future-ready GCC leadership will be:
- Resilient under ambiguity
- Digitally fluent, not just digitally aware
- Inclusive by design
- Outcome-focused, not task-oriented
- Capable of creating a learning culture, not just managing one
The CHRO’s influence is central to shaping this profile.
Transforming Leadership Is the Real Digital Strategy
We often talk about digital transformation, but without leadership transformation, it’s just automation. GCCs need leaders who can unlock exponential value, not just optimize processes.
The time is now for CHROs to:
- Challenge outdated leadership norms
- Drive cultural rewiring
- Build innovation-ready mindsets
- Make leadership transformation a strategic priority
Because at the heart of every great GCC is not just great talent or great tech, but transformational leadership that turns ambition into impact.
10 Best Leadership Skills Every Professional Should Know in 2026
Today, leadership is in crisis. Workers are losing faith in leaders because many just aren’t measuring up.
DDI Global Leadership Forecast 2025 states that the trust in management fell from 46% in 2022 to as low as 29% in 2024, an enormous plunge. It shows how much everybody distrusts their leaders now.
While so much of the world is changing at the speed of light due to technology and remote work, leaders are still blamed for lacking rudimentary human competencies such as empathy and clear communication, which are one of the best leadership skills.
If you examine legendary leaders throughout history, you will see that they possessed these competencies in abundance. Today, far too many leaders lack these competencies.
Then, what do today’s professionals need to learn to keep up with today’s requirements and thrive amidst all this change? This blog will discuss the 10 most critical leadership skills required in 2026 and how to develop them.
What Are the Best Leadership Skills in India and Southeast Asia?
In India and Southeast Asia, the best leadership skills in combine emotional intelligence, digital and AI literacy, adaptability, inclusive communication, and change leadership. These skills enable leaders to manage large, diverse, hybrid workforces while scaling talent development and business performance effectively.
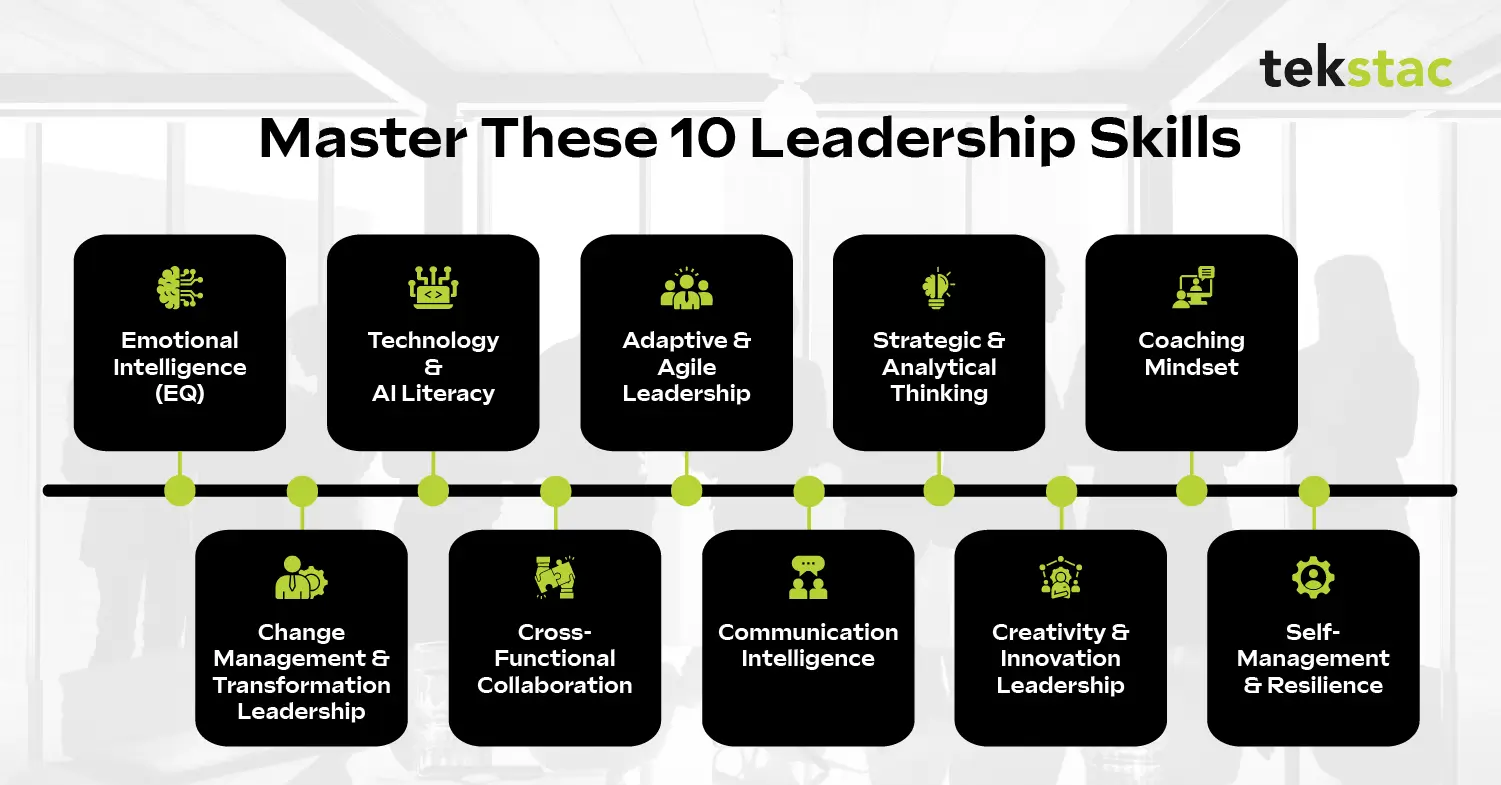
10 Best Leadership Skills Every Professional Needs in 2026
One must observe that some leadership qualities are never so old. Empathy, communication, and trust have been the pillars of good leadership and will forever be.
But the world keeps evolving at this fast pace, and with it, the kind of skills leaders need. For example, computer literacy was not as critical previously as it is today. Today, the skill of coping with AI and technology is what any leader needs. With new opportunities and challenges by 2026, leaders will have to change and evolve.
- Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
- Technology & AI Literacy
- Adaptive & Agile Leadership
- Strategic and Analytical Thinking
- Coaching Mindset
- Change Management and Transformation Leadership
- Cross-Functional Collaboration
- Communication Intelligence
- Creativity and Innovation Leadership
- Self-Management and Resilience
1. Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
What if it is possible to be a good leader through emotional understanding? Emotional Intelligence (EQ) has already passed from being a soft skill to being the basis of fearless leadership. EQ is about paying attention to your feelings and others’, managing your reactions, and establishing genuine relationships.
In the age of AI dominance, we cannot live without trust and empathy. EQ leaders create psychologically safe environments, with collaboration and innovation thriving even when teams are separated by geography across continents. For instance, the most incredible testimony to Satya Nadella’s Microsoft transformation is where he created the learning and empathy culture and re-stoked the growth and morale of the company.
How to build it: Practice vulnerability by opening up your problems. Always consider your emotions, and ask your colleagues for straightforward opinions to become sensitive to forming relationships. Practice empathy daily.
2. Technology & AI Literacy
Talent in 2026 will need to ride the wave of AI. 71% of CEOs in Korn Ferry’s 2025 Global Workforce Survey are confident that AI will add value to their worth within three years. Leaders today must have first-hand experience with AI and new technology. This skill enables them to identify improvements in efficiency, anticipate risk, shape responsible use of AI, and increase the agility and creativity of decision-making.
This leads to more effective decision-making and facilitated groups of de-drudged work. Amazon’s early implementation of AI to maximize logistics set industry standards and pushed hyper-growth revenue, demonstrating tech know-how pays.
How to build it: Get AI and digital literacy skills training, engage with tech forums, and collaborate with internal experts to stay competitive.
3. Adaptive & Agile Leadership
Most leaders are playing catch-up on talent as though it were 2010, and their leadership is outdated. John Maxwell’s book, Leadershift, is about leaders shifting their style so they can keep up with the pace of a changing world. Adaptive leaders create a culture where teams learn fast, turn fast, and embrace failure as a stepping stone.
For example, Netflix’s transition from DVD rentals to streaming is a quintessential example of agile leadership, making an early bet on video streaming revolutionized the company and kept it ahead of the curve.
How to build it: Condition yourself to be agile in mind by exposing yourself to something new and getting a great many different ideas every day.
4. Strategic and Analytical Thinking
Strategic thinking is seeing the big picture, connecting the dots, and making well-thought-out decisions driven by long-term organizational goals. This is reinforced by analytical thinking, which assists leaders in filtering information, identifying trends, and projecting possible risks or opportunities. With increasingly dynamic markets and data being the default norm, leaders possessing such skills create lasting competitive advantages.
As Jim Collins notes in Good to Great, disciplined strategic thinking is a defining trait of companies that outperform others over the long term. Among the best leadership skills, this capability helps leaders move beyond short-term fixes and set goals based on objective analysis. It enables cost-effective resource allocation, clear prioritization, and confident decision-making amid uncertainty.
How: Work actively with information, encourage shared goal-setting, and test assumptions regularly. Acquiring skills in applying decision-making templates and thinking about alternative perspectives requires applying those skills to build them.
5. Coaching Mindset
Leaders’ actions are shifting from commanding and controlling to empowering and constructing. The coaching method can be implemented through good questions, listening, and nudging others to their solutions. Jacob Morgan outlines in his book The Future Leader that this shift is a necessity as workplaces become more complicated and growing talent is priority number one.
By 2026, coaching will play a critical role in employee training by building trust, boosting motivation, and accelerating learning across teams—especially in distributed or hybrid organizations. This approach enables leaders to develop autonomy, encouraging employees to innovate, take initiative, and apply new skills effectively on the job.
Organizations like Google have demonstrated the impact of performance enhancement with coaching in projects like Project Oxygen, which found that managers’ coaching styles strongly impact team performance.
How to develop: It can be achieved through regular growth conversations, emphasis on development and strengths areas, and a culture of continuous learning.
6. Change Management and Transformation Leadership
Change is inevitable, but outstanding leaders can make change an imperceptible evolution and not an interruption. Change management skills involve facilitating teams through change phases, breaking down resistance, and maintaining momentum to achieve desired results. It is especially important in the aftermath of AI, hybrid workplaces, and digital shifts that are redefining companies.
By 2026, open-speaking leaders who can speak to their teams in advance and establish psychological safety will facilitate more adoption and maintain productivity amid change. This leadership skill also reduces fear and increases resilience in organizations.
Taking Microsoft as an example, its transformation under Satya Nadella as a change leadership story of a software giant becoming a cloud giant could be an example of the best type of change leadership. Nadella’s open communication and guidance pushed employees toward acquiring alternative thinking and operational outlooks.
How to construct: Leaders learn good change management by observing best practice models, constructing empathic conversations and involving stakeholders at all change levels.
7. Cross-Functional Collaboration and Participative Decision-Making
Inclusive decision-making involves seeking alternative perspectives to enhance thinking and avoid blind spots. Cross-functional teamwork breaks down silos, speeds up execution, and puts teams on purpose. Korn Ferry discovered that 43% of senior leaders experience impostor syndrome, which inhibits full participation, rendering inclusivity even more important to unlock collective leadership potential.
Leaders who practice inclusive leadership skills by creating space for employees to be heard foster innovation and accelerate business outcomes. Salesforce is a strong example, where a focus on diversity and inclusion has strengthened culture while delivering sustained financial performance.
How to build: Daily collaboration habits, constructing psychological safety, and learning decision-making approach to create inclusive input.
8. Communication Intelligence
Clear, open, and emotionally smart communication is the foundation of great leadership. Companies are only just beginning to figure out how to work hybrid and run at speed, and communication intelligence keeps people on track, engaged, and energized. It’s not about communicating, but communicating in such a way as to speak to people’s emotions and build trust.
Netflix’s communication culture and reward culture is a classic example of communication contributing to innovation and accountability.
How to create: Embed frequent feedback loops, role-playing narratives, and sensitivity to body language even in virtual environments.
9. Creativity and Innovation Leadership
No matter how much participation is augmented by AI, human ingenuity remains the best equalizer in leadership. Creativity is all about generating fresh ideas, while innovation is the way one converts those ideas into feasible products, services, or processes. Structured or disciplined creativity is what Jim Collins calls the answer to the Great to Good companies.
Among the most important leadership skills is the ability to create environments where experimentation is encouraged, failure becomes a source of learning, and diverse viewpoints are valued. This approach drives teams to develop innovative solutions and deliver more compelling customer experiences. Apple’s culture of innovation demonstrates how creativity-driven leadership enables companies to remain industry leaders year after year.
How to build: Provide room for brainstorming, enable cross-functional collaboration, and freely reward creative efforts.
10. Self-Management and Resilience
Self-management, emotional, mental, and physical is the recipe for long-term success. Self-management requires emotional control, stress control, and keeping your focus in the midst of trouble. Resilient leaders need to practice the behavior they want their teams to embody.
How to construct: To construct this capability, one needs to develop reflective habits, practice intentionally, and establish sharp boundaries between play and work.
How to Develop Leadership Skills That Truly Matter
Genuine leadership development starts with knowing yourself. Maybe you have discovered that your employees are not as invested as they might be. Maybe you are having a hard time leading during the constant flux.
Leadership does not happen naturally. Leadership is a skill set, a checklist of habits, and attitudes that you learn with time. Begin by asking for counsel from your teammates or colleagues. Listen to how you are handling challenges. Are you listening too little? Are you responding quickly enough? Making space for other people’s voices and ideas? Then, learn something new every day. Whether it is reading, mentoring, learning online courses, or simply observing good leaders ahead of you, every one counts. And as you grow, take your people with you. Great leaders do not raise themselves alone, they raise people alongside them.
Hence, leadership competence, which is anchored in the best leadership skills, is what differentiates a bad leader from a great one. It is the set of attitudes, behavior, experience, and competences that enables you to lead with influence, particularly in a digital-first world.
FAQs on Best Leadership Skills
1. What are examples of leadership skills at work?
Examples of leadership skills at work include emotional intelligence in team interactions, clear communication during change, data-driven decision-making, coaching employees for performance improvement, and cross-functional collaboration. For L&D leaders, these skills show how learning translates directly into day-to-day leadership effectiveness.
2. What are the 5 qualities of good leaders?
The five core qualities of good leaders are emotional intelligence, adaptability, strategic thinking, effective communication, and integrity. For L&D teams, these qualities guide leadership development programs that build trust, improve performance, and support long-term organizational growth.
3. What is the most important leadership skill in 2026?
Emotional intelligence is the most important leadership skill in 2026. As AI, automation, and hybrid work expand, leaders who demonstrate empathy, self-awareness, and strong interpersonal skills are better equipped to engage employees and maximize the impact of learning initiatives.
4. Can leadership skills be learned?
Yes, leadership skills can be learned through structured employee training, coaching, feedback, and real-world practice. L&D leaders play a critical role in designing continuous, skills-based learning experiences that help professionals develop and apply leadership capabilities over time.
Top 3 Blended Learning Benefits That Make It Perfect for Millennials and Gen Z
Traditional education is dead. At least, that’s what your attention span is telling you when you’re forced to sit through another three-hour lecture. Today’s learners—especially Millennial, Gen Z, and the upcoming Gen-Alpha—don’t need motivation to learn.
They need systems that respect their time and actually deliver results.
Blended learning benefits offer exactly that: an innovative fusion of digital flexibility and human interaction that matches how modern minds actually work.
Why a Custom Approach Helps Every Learner?
Blended learning is not just throwing Zoom calls at traditional classrooms and calling it innovation. Real blended learning combines digital efficiency with human insight to create learning experiences that actually stick.
- Personalized Learning Experience: Everyone learns differently, and blended learning recognizes that by adjusting the pace and style so each person can truly grasp every topic without feeling left behind.
- Hybrid Learning Approach: This method brings together the best of both worlds, letting technology handle the routine parts while face-to-face time is used for solving real problems and answering tough questions.
- Building a Lifelong Learning Mindset: Blended learning encourages curiosity and growth, making it easier to pick up new skills whenever needed and stay ready for whatever comes next in life or work.
- Immediate Feedback and Practical Use: Whether it’s a quick automated check or a teacher’s advice, feedback comes fast, so mistakes are fixed early and new skills can be put into practice right away.
- More Engagement, Less Boredom: With interactive lessons, hands-on projects, and group work, blended learning keeps everyone interested and motivated—not just memorizing facts, but actually learning to solve problems.

This hybrid learning approach recognizes a simple truth: not everything needs to happen in a classroom, and not everything should happen behind a screen. Recent 2025 data shows that approximately 73% of students say e-learning enables them to study at their own pace, highlighting a strong preference for formats beyond traditional one-mode teaching.
Why Traditional Learning Fails the Digital Generation
Gen Z learners don’t start with theory when solving problems. They search for the problem on Google, watch a 3-minute tutorial, try something immediately, and iterate rapidly based on results.
Traditional education punishes this natural learning behavior by forcing linear progression and treating exploration as cheating. Blended learning benefits embrace digital-native approaches through:
- Search-first solving: Learners can jump between online resources and human guidance without penalty or restriction.
- Immediate application: Concepts get tested through hands-on projects rather than being delayed until semester-end assignments.
- Rapid iteration: Mistakes become learning opportunities with instant feedback rather than delayed grade penalties.
- Community-driven solutions: Peer networks and forums supplement formal instruction with real-world problem-solving approaches.
- Non-linear progression: Advanced learners can skip ahead while others get additional support without holding back groups.
3 Key Benefits of Blended Learning Programs
- Personalized Learning Experience
- Hybrid Flexibility (Online + Offline)
- Lifelong Learning Mindset for Career Growth
1. The Power of Personalized Learning Experience
Your personalized learning experience isn’t about choosing between light and dark mode—it’s about systems that adapt to how you actually learn and perform.
Innovative blended platforms track time spent on individual challenges, common error patterns across multiple attempts, preferred learning formats, and peak performance hours when focus is strongest.
This data actively shapes your next learning session:
Adaptive Content Delivery
- Struggling concepts: Receive additional practice problems and alternative explanations tailored to your learning style.
- Advancing quickly: Skip redundant content and move to advanced concepts that challenge the current skill level.
- Visual learning: Get video explanations and interactive demonstrations before text-based theoretical material.
- Human interaction needed: Get matched with mentors who specialize in your specific challenge areas.
The system becomes your learning assistant, not your taskmaster demanding compliance with rigid schedules.
2. Hybrid Learning Approach: Best of Both Worlds
The magic happens when online and offline elements work together strategically rather than operating as separate, disconnected experiences.
Online Components Handle:
- Core concept delivery: Complex topics broken into digestible pieces that respect attention spans and busy schedules.
- Self-paced practice: Learners can repeat difficult sections without embarrassment while getting instant validation on progress.
- Progress tracking: Visual indicators of growth that motivate continued engagement rather than arbitrary completion percentages.
- Resource libraries: Reference materials, code examples, and troubleshooting guides are available during real-world application moments.
Offline Components Focus On:
- Complex problem-solving: Collaborative sessions where different perspectives illuminate solutions that individual study might miss.
- Project reviews: Human mentors provide context-specific guidance that automated systems cannot replicate effectively.
- Peer collaboration: Working with others on practical problems that mirror actual workplace scenarios.
- Career mentorship: Experienced professionals provide industry insights and strategic guidance for long-term growth planning.
3. Building a Lifelong Learning Mindset Through Blended Approaches
Lifelong learning mindset isn’t just a corporate buzzword—it’s economic survival. Skills become obsolete faster than ever, and successful learners adapt quickly to changing requirements.
Blended learning benefits support continuous growth by removing time constraints that prevent working professionals from upskilling effectively, while providing just-in-time learning when specific skills are needed for immediate projects.
Practical Implementation Strategies:
- 20-minute blocks: Start with focused learning sessions that fit into busy schedules without overwhelming daily responsibilities.
- Project-based outcomes: Focus on tangible results that demonstrate competency rather than participation trophies with questionable market value.
- Join cohorts: Community support that provides accountability and shared struggle during difficult learning phases.
- Apply skills immediately: Reinforce learning through practical application rather than waiting for perfect conditions or permission.
- Document progress: Create evidence of growth that builds confidence and demonstrates capability to potential employers.
The Neuroscience Behind Why Blended Learning Works
Your brain doesn’t learn in straight lines. Research from the Journal of Educational Psychology shows that varied learning contexts improve retention by up to 40% compared to single-format instruction.
Blended learning benefits align with natural information processing through spaced repetition, where online modules reinforce concepts over time while offline sessions provide different contexts for the same skills, creating emotional connections to abstract ideas.
Active recall replaces passive consumption:
- Problem-solving focus: Engagement with challenging tasks that require thinking rather than passive information consumption.
- Peer discussions: Teaching others in your own words solidifies understanding and reveals knowledge gaps.
- Immediate application: Real-world usage exposes the difference between recognition and proper comprehension.
Real-World Success Metrics That Matter
Forget completion rates and quiz scores. Blended learning benefits show up in metrics that actually impact careers and personal growth.
Portfolio development with tangible projects demonstrates competency more effectively than certificates, while skill application in current roles within 30 days proves learning transfer to practical situations.
Learning Efficiency Measures:
- Time to competency: Faster skill acquisition through focused, practical learning approaches rather than theoretical foundation building.
- Retention rates: Skills that stick because they were learned through application rather than memorization.
- Problem-solving speed: Ability to apply knowledge quickly when faced with actual challenges rather than artificial test conditions.
- Transfer ability: Flexible thinking that adapts learned concepts to new situations and unexpected problems.
Ready to Experience Real Learning Transformation?
The era of sitting through boring lectures and hoping for the best is over. Blended learning benefits offer a clear path to skills that actually matter, delivered in ways that respect your time and intelligence.
Your competition isn’t just learning the same skills you are. They’re learning how to understand better, faster, and more effectively than traditional methods allow.
Stop wondering if there’s a better way to learn. Start experiencing the transformation that happens when technology and human insight work together seamlessly.
Discover how our blended learning approach can accelerate your skill development—request a demo today.
Career Progression Plans: Aligning Employee Goals with Business Objectives
Why Traditional Career Progression Plans Fail
Your best engineer just left.
Again. Official reason?
“Looking for better growth opportunities.” But let’s be real, they just couldn’t see a future here.
Now the team’s left picking up the pieces, and you’re stuck trying to figure out promotions with half-baked feedback and gut calls. You’re hoping you’re getting it right, but deep down, you’re not sure.
And it’s not just about losing one person. It hits harder, and morale dips. Work slows down.
The problem?
Most career progression plans are just broken. Too much guesswork. Too much politics. Not enough clarity or fairness.
So yeah, it’s not just a one-off. It’s a pattern. And if nothing changes, the best people will continue to walk out the door.
The Brutal Reality Behind Failed Career Systems
Here’s what’s happening in your organization under the guise of employee career development:
- The visibility trap: The ones who speak up the most often get noticed. They get promoted. Meanwhile, the quiet high-performers keep delivering real results but stay under the radar. Over time, that lack of recognition turns into quiet frustration. The potential is there, but it’s left untapped.
- The title inflation game: New senior titles keep getting created, but nothing changes in the work or responsibility. It just adds noise. Teams often get confused, and external candidates struggle to understand the actual meaning of these titles.
- The management bottleneck: Every promotion or role change depends on managers who are already overloaded. They are short on time and stretched to the limit. That leads to delays, inconsistent decisions, and people feeling stuck without a clear way forward.
- The skill speculation problem: People are being judged based on assumptions or how they perform in interviews rather than on real, proven work. This leads to mismatched roles, frustration, and a disconnect between potential and performance.
Research from Deloitte shows that replacing a senior engineer can cost up to twice their annual salary, but the real damage is the knowledge walking out the door, stalled projects, and demotivated remaining teams.
Build Career Progression Plans That Work
It’s time to treat career development like a well-engineered system—methodical, data-driven, and continuously evolving.
- Map Observable Skills, Not Fluffy Titles.
- Design Flexible Career Progression Plans, Not Ladders.
- Replace Annual Reviews with Continuous Evidence Collection.

1. Map Observable Skills, Not Fluffy Titles
Define what people can do—don’t rely on vague titles.
- Concrete capability clusters: For example, “designs and deploys scalable microservices capable of handling over ten thousand concurrent users with high uptime” provides leaders with clarity and engineers with purpose.
- Real-world problem complexity: Track someone’s ability to identify and resolve tricky production race conditions under pressure rather than just attendance or code volume.
- Context‑specific abilities: Recognize that excelling at legacy refactoring is different from greenfield architecture; both deserve acknowledgment, but they require clarity of context and measurement.
- Measurable depth indicators: Map progression from “needs guidance to implement” up through “independently leads and mentors peers on advanced patterns across projects.”
2. Design Flexible Career Progression Plans, Not Ladders
People don’t grow in straight vertical ladders—they flourish across diverse, evolving career pathways.
- Multiple advancement paths: Create distinct tracks, such as technical specialist, engineering lead, or systems architect, allowing engineers to grow based on impact rather than role or hierarchy.
- Lateral skill expansion: Enable transitions, QA engineers developing DevOps proficiency, backend developers learning security best practices, or data analysts moving into product analytics without penalizing them for sideways moves.
- Diagonal capability building: Encourage growth at the intersection where senior developers adopt product thinking or engineers begin to develop core business strategy acumen, bridging gaps across teams.
- Dynamic role evolution: Refresh and adjust tracks quarterly to reflect changing priorities, new tech stack investments, or emerging business needs, keeping growth aligned with the company’s direction.
3. Replace Annual Reviews with Continuous Evidence Collection
Why evaluate performance once annually when engineers are evolving daily?
- Project-based skill demonstration: Every code review, production deployment, and architecture session becomes a data point that evidences capability development and tangible impact on business outcomes.
- Peer validation mechanisms: Structure input from the teammates who work with someone every day. This gives a much clearer picture of how they collaborate and how much trust they’ve earned within their domain, compared to just relying on top-down reviews.
- Real-time capability dashboards: Make individual progress visible to engineers, managers, and leaders alike, highlighting strengths, areas for growth, and potential next steps at any time.
- Transparent progression criteria: Publicly share what’s required to advance to the next level, removing guesswork, bias, and inconsistency in promotions or recognition.
Embed Talent Management Strategy with Business
This is not a nice-to-have. It’s a competitive business advantage when engineers’ growth aligns with organizational growth goals.
- Align skills with business direction: Don’t invest in declining languages or tools. Focus on where your roadmap is headed, whether it’s AI platform development, full-stack expansion, or reliability engineering.
- Future‑focused capability building: If your strategy includes an AI-native architecture, build machine learning fluency across engineering teams, not just within one silo, through targeted learning paths and live projects.
- Platform transformation readiness: While migrating to cloud-native systems, fast-track engineers who have already demonstrated the ability to work with microservices architecture, container orchestration, and resilience patterns.
- Cross‑functional bridge building: Encourage engineers to speak product language, especially when customer experience becomes the competitive edge, improving communication, alignment, and solution quality.
Strategic workforce intelligence: Use real-time, anonymized skill data to answer critical questions: “Are we technically ready for our next 18-month roadmap? Who’s closest?“—without gut guessing.
Make Succession Planning Engineering‑Grade, Not Crisis‑Driven
When leaders leave, don’t scramble. Plan ahead.
- Capability trajectory tracking: Spot the people who are growing in both technical depth and influence across the team. This helps you understand who might be ready for bigger roles before you’re forced to make urgent decisions.
- Experience gap bridging: Give engineers the kind of stretch opportunities that actually prepare them for what’s next. Let them lead cross-team architecture reviews or take on client-facing technical demos so they’re ready when the time comes.
- Leadership pipeline visibility: Make it easy for leaders to see where their teams stand. Show them who’s ready, who could step up next, and where the risks are so that they can plan with clarity and confidence.
Measure What Matters
Ditch HR vanity metrics—track indicators reflecting real system health and strategic impact.
- Internal promotion rate: Measure the proportion of senior roles filled internally versus externally, highlighting the health of organic career development.
- Capability development velocity: Track the rate at which engineers acquire mission-critical skills aligned with your current and future strategic needs.
- Cross-team mobility success: Monitor whether staff are moving between domains to share knowledge or are trapped in silos with stagnant role paths.
- Retention correlation: Analyze whether professionals moving along defined, capability-based tracks stay longer than those in outdated, hierarchical systems.
Employee Upskilling and Reskilling That Works in Context
Forget generic courses—build learning into everyday work.
- Business needs-based skill development: Recommend learning content tied directly to upcoming project tasks and role requirements rather than generic catalogs.
- Work‑embedded practice: Integrate skill reflection into sprint retrospectives, design reviews, and daily standups, making learning part of engineering flow.
- Mentorship as a growth multiplier: Develop structured peer coaching where senior team members both coach and refine their leadership through active mentoring.
- Evidence‑based learning outcomes: Track which learning efforts (courses, projects, peer-teaching) correlate with actual performance improvements and promotion readiness.
The best engineers don’t just want a title; they want a Career Progression Plan that’s visible, practical, aligned to impact, and personally meaningful. Help them see the art, science, and movement of their career. Do that, and you’ll stop losing great people to uncertainty.
Interested in seeing how this works in real engineering organizations without adding unnecessary layers or meetings?
Get a personalized demo of Tekstac. Skills, growth, outcomes—all stitched together by design, not guesswork.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting a Skills Assessment for Employee Training
In many organizations, productivity appears high: projects are delivered, deadlines are met, and teams stay busy. But behind this facade of activity often lies an uncomfortable question: Are people truly working in alignment with their actual skills?
The answer, more often than not, is “not really.”
Roles are frequently assigned based on resumes, past job titles, or assumed experience, not based on validated, current capabilities through a proper Skills Assessment. That’s where the inefficiencies start to creep in. Over time, these assumptions evolve into a quiet but dangerous problem: skill blindness. Our Skills Assessment Guide can help you break this cycle by identifying real skill gaps and aligning talent more effectively.
What is a Skills Assessment?
A Skills Assessment is a structured and data-driven method that organizations use to understand the current skills of their employees and compare them with the skills required for their roles. Instead of relying on assumptions, job titles, or intuition, a Skills Assessment provides clear, measurable insights into workforce strengths, skill gaps, and development needs.
A typical Skills Assessment includes:
- Mapping role-based skills and competencies
- Evaluating employees in real or simulated work environments
- Using objective scoring and benchmarks to measure performance
- Analyzing results to guide hiring, upskilling reskilling, and performance decisions
In simple terms, it removes guesswork and helps companies make smarter decisions about talent alignment, learning investment, and productivity improvement.
What Is Skill Blindness and Why Does It Hurt Performance?
Without a structured Skills Assessment strategy in place, organizations end up guessing their way through talent deployment. That guesswork may hold up for a while, but eventually, it snowballs into misaligned responsibilities, inefficiencies, and burnout.
Take this example: A software development team consistently lags behind deadlines.
The assumption is they need more staff. So leadership hires aggressively. Yet the problem persists. The real issue? A misalignment between skill sets and project demands, not the headcount.
Without proper Employee skill gaps analysis, you risk:
- Promoting high performers without recognizing the full extent of their capabilities
- Letting underperformers struggle silently without targeted support
- Investing in training programs that fix the wrong problems
This leads to:
- Reactive upskilling and reskilling strategies, not proactive ones
- Employee performance reviews that lack data and meaning
- Leadership decisions based on output symptoms, not root cause analysis
Ultimately, you can’t optimize what you can’t measure. And measuring skills is the foundation for building an adaptable, competitive workforce.
“Shockingly, only 14% of business executives strongly agree that their organization is using the workforce’s skills and capabilities to their fullest. (Deloitte)”
Why Do Organizations Need a Structured Skills Assessment?
To eliminate these pitfalls, companies must adopt a structured, repeatable, and data-driven Skills Assessment framework.
A robust Skills Assessment strategy provides:
- Clarity about current capabilities
- Transparency in decision-making
- Alignment between business goals and employee skill sets
- A culture of continuous learning and growth
But it’s not about generic surveys or one-time testing. True Skills Assessments are ongoing, role-specific, and aligned with real-world performance.
How Do You Build a Skills Assessment Process? (Step-by-Step Guide)
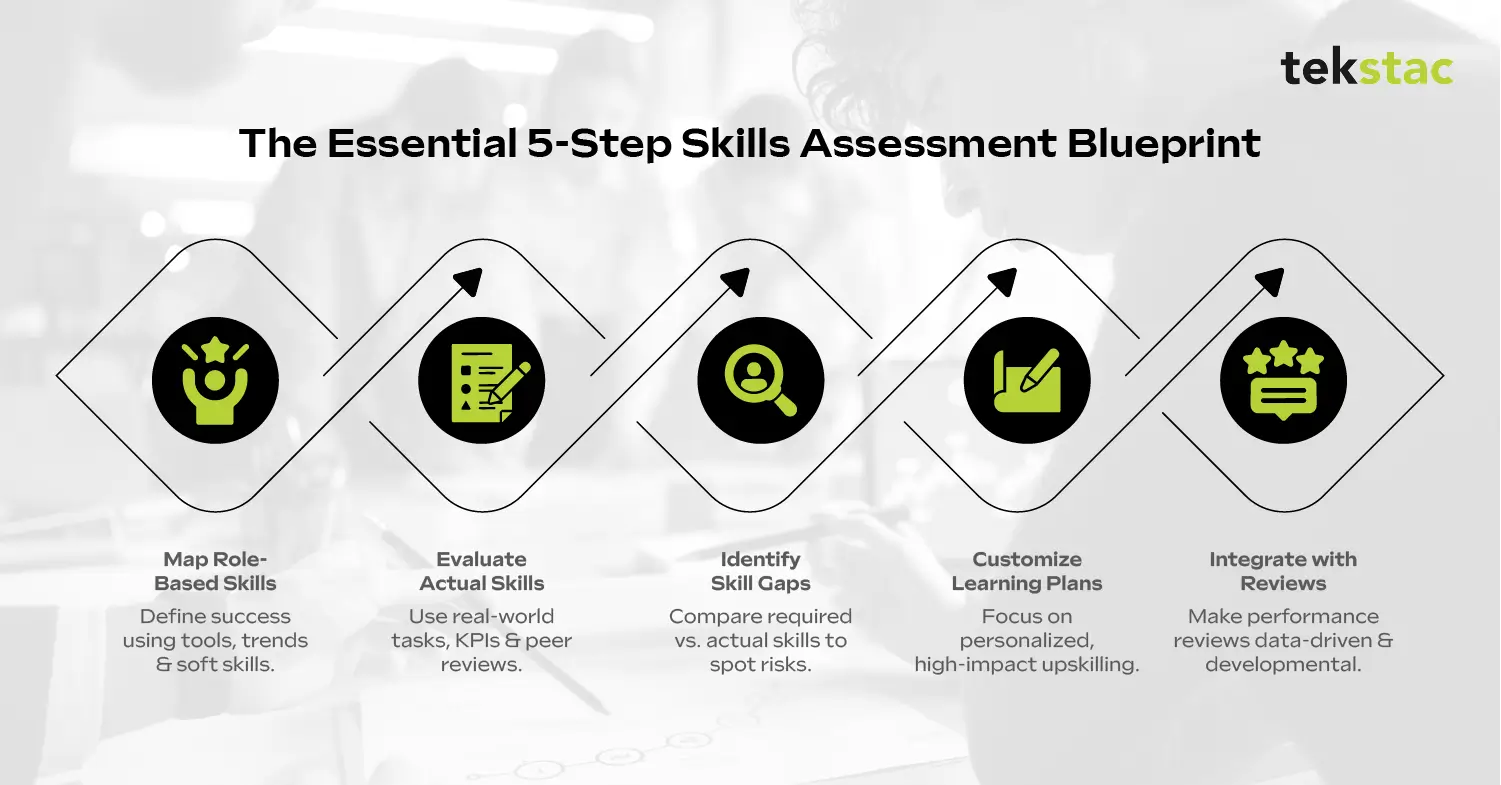
1. Map Required Skills by Role
Start by defining what success looks like in each role.
Don’t just rely on generic job descriptions. Factor in:
- Current tools and technologies
- Industry trends and compliance requirements
- Soft skills like communication or leadership
Core technical competencies tied to business impact
2. Assess Actual Skill Levels
Assessments should be performance-based, not theoretical. Combine:
- Real-world simulations (like coding tasks or client mock calls)
- Project retrospectives
- Peer reviews
- Objective KPIs
This holistic view reveals not just what someone knows—but how they apply it.
3. Conduct an Employee Skill Gap Analysis
Once both the “required” and “actual” skill levels are clear, it’s time to identify gaps.
Ask:
- What are the top skills missing from key roles?
- How wide is the gap? (scale it numerically for prioritization)
- What business risks are associated with each gap?
Tools like Tekstac offer actionable dashboards that visualize these gaps for informed planning.
4. Tailor Upskilling and Reskilling Strategies
Use the gap data to design interventions that are:
- Specific: Tied to one skill or behavior
- Personalized: Aligned to individual learning styles and levels
- Timely: Delivered as just-in-time learning or through projects
Avoid generic training modules. Go for high-impact courses, mentorship, job rotations, or AI-driven microlearning.
5. Loop It into the Employee Performance Review Process
Instead of treating Employee performance reviews as standalone rituals, integrate updated Skills Assessment data.
This:
- Makes reviews more evidence-based
- Helps managers plan career paths
- Encourages employees to take ownership of their learning journey
Skills Assessment Case Studies: How Leading Companies Apply It
1. IBM – Building a Culture of Upskilling Through Skill Assessments
IBM implements continuous skill assessments across departments. This enables:
- Real-time tracking of skills in demand
- Targeted upskilling programs
- Enhanced internal mobility for employees based on skill readiness
The result? A future-ready, agile workforce and improved employee retention.
2. Google – Precision in Tech Hiring Through Skill-Based Evaluation
Google integrates hands-on coding assessments with interviews. This dual approach:
- Ensures practical, not just theoretical, expertise
- Reduces hiring errors
- Encourages diversity by focusing on ability over background
Google’s model highlights how customized role-specific assessments lead to better hires.
3. Amazon – Scaling Skill Validation Across Thousands of Candidates
Amazon uses data-driven, scalable skill assessments in both tech and non-tech roles. Their success lies in:
- Automating assessments at scale
- Using analytics to refine test content
- Applying assessments to both hiring and internal promotions
This has streamlined their high-volume recruitment while ensuring role alignment.
What Is the Strategic Value of Skills Assessment for Organizations?
By now, it’s clear: building a Skills Assessment framework isn’t just about checking boxes, it’s about creating a high-performance learning culture.
The benefits include:
- Accurate Employee skill gap analysis
- Informed employee performance reviews
- Strategic upskilling and reskilling strategies
- A boost in retention, engagement, and innovation
How Do You Choose the Right Skills Assessment Tools?
Effective Skills Assessment isn’t just about methodology—it’s about execution. For that, you need the right platform.
An ideal tool should offer:
- Role-based assessments for accuracy
- Real-world simulations for credibility
- Analytics and benchmarks for decision-making
- Integration with LMS and HRMS for workflow continuity
One platform that delivers across these fronts is Tekstac.
Why Tekstac Is the Best Platform for Enterprise Skills Assessment
Tekstac provides a comprehensive platform designed specifically for organizations aiming to execute a structured Skills Assessment strategy. Here’s how it maps directly to your needs:
Role-Based Skill Assessments
Tekstac aligns its evaluation modules with specific job functions. This means:
- A data scientist is assessed on ML proficiency, data handling, and tool familiarity
- A sales professional is tested on objection handling, CRM use, and negotiation skills
This relevance ensures accurate insights, not guesswork.
Real-World Coding Simulations
For technical roles, Tekstac provides live coding environments that simulate real business challenges. This tests:
- Logical thinking
- Clean code principles
- Time management under pressure
Automated Grading and Benchmarking
Using smart algorithms, Tekstac automates evaluations. No more manual checks. The platform also benchmarks individual performance against:
- Team averages
- Industry norms
This lets you see exactly where your talent stands competitively.
Actionable Analytics
One of the standout features of Tekstac is its data visualization engine. Leaders get:
- Clear dashboards on skill distributions
- Heat maps of critical skill gaps
- Recommendations for learning interventions
Seamless Integration with LMS/HRMS
Tekstac doesn’t replace your existing systems—it enhances them. It can plug into:
- SAP SuccessFactors
- Workday
- Moodle
- Other enterprise LMS/HRMS platforms
This ensures that Skills Assessment becomes part of your daily workflow, not an isolated event.
Common Concerns About Skills Assessment—and How to Overcome Them
Even when leaders understand the value, adoption of a Skills Assessment system is often delayed due to concerns. Let’s tackle them head-on.
Concern 1: “It’s Too Resource-Intensive”
Reality: While the initial investment requires time and effort, the return is exponential.
- Accurate Employee skill gap analysis reduces wasted training budget
- Productivity improves as tasks align with talent
- Turnover drops when employees feel properly utilized
Think of it as building a foundation for everything: learning, staffing, innovation.
Concern 2: “Employees Will Feel Threatened”
Reality: If framed incorrectly, yes. But the key is intentional communication.
- Emphasize growth, not judgment
- Position assessments as tools for career progression
- Highlight success stories where employees unlocked new roles due to their hidden talents
You’re building a feedback-rich culture, not a punitive one.
Concern 3: “It’ll Be Outdated Fast”
Reality: This is where tools like Tekstac excel.
Their assessment libraries can be updated regularly to reflect:
- New technologies
- Regulatory changes
- Internal strategy shifts
Additionally, since assessments are data-driven, you can adapt based on live skill evolution.
Concern 4: “Integration Will Be a Nightmare”
Reality: With modern APIs, platforms like Tekstac make integration nearly frictionless.
They offer plug-and-play compatibility with popular platforms, ensuring that:
- HR teams don’t juggle multiple tools
- Employees have a seamless experience
- Data flows directly into your performance management systems
How to Implement a Continuous Skills Assessment Loop
Now that tools and objections are covered, here’s a practical execution roadmap to embed Skills Assessment into your culture.
Step 1: Start With a Pilot Program
Choose a single department (e.g., engineering or sales). Use Tekstac to:
- Run a baseline skill evaluation
- Identify critical skill gaps
- Deliver personalized training based on the results
Measure outcomes (project success, engagement scores, peer feedback) to validate the ROI.
Step 2: Align Assessments with Learning Paths
Connect results directly to upskilling and reskilling strategies. Whether you use internal academies or external platforms, make sure the learning paths solve for actual, identified gaps.
Step 3: Integrate with Performance Reviews
Bring the Skills Assessment data into regular employee performance reviews.
- Use it to validate strengths
- Create development plans with measurable milestones
- Identify high-potential employees for stretch assignments or promotions
Step 4: Scale Organization-Wide
After validating with one unit, roll out across departments.
Best practice: staggered implementation with champions from each team. This improves adoption and reduces pushback.
Long-Term Benefits of Continuous Skills Assessment
Once fully embedded, Skills Assessments become part of your company DNA. The long-term benefits include:
- Better succession planning
- Enhanced internal mobility
- More targeted hiring
- A resilient workforce capable of shifting with the market
You also create a learning culture where development is tied to real business outcomes, not just hours logged in training portals.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Skills Assessment
In a business environment, the difference between surviving and thriving lies in your workforce adaptability. A structured Skills Assessment framework is not just a tool, it’s your organization’s compass for growth, relevance, and competitive edge.
It enables you to:
- Replace guesswork with data
- Empower employees through transparency
- Align training with real business needs
- Prepare for the future, not just react to the present
Tekstac offers a powerful, customizable engine to help you implement this vision, from employee skill gap analysis to role-specific learning. The time to move from assumptions to action is now.
FAQs on Skills Assessment Guide
1. What is a Skills Assessment framework?
A Skills Assessment framework is a structured approach to evaluate employee competencies and identify skill gaps for development.
2. What is the difference between Skills Assessment and resume-based hiring?
Resume-based hiring relies on claimed experience, while skills assessment measures real, proven capabilities through practical evaluations.
3. Why is a Skills Assessment strategy important for upskilling and reskilling?
It helps pinpoint existing skills vs. needed skills, enabling targeted learning programs and better workforce readiness.
4. What role does skills assessment play in performance reviews?
It provides objective data on strengths and improvement areas, supporting fair evaluations and personalized development plans.
ADDIE Model Explained: Step-by-Step Talent Development Framework
Almost half of the skills possessed by the present workforce is likely to become outdated in a mere two years.
Now, organizations have a challenge: “How do we continuously build talent in order to catch up with technological advancements?”
Most organizations tend to respond to skill shortages only after they have significantly affected performance, causing expensive delays. There’s a need for a disciplined, systematic approach to talent development that deals with business needs as they occur but also prepares for future requirements.
The ADDIE model provides a framework to design such learning programs. In this blog, let’s discuss in-depth how this model functions and how you too can apply ADDIE to talent development in 2026.
What Is the ADDIE Model? Definition and Why It Matters in 2026
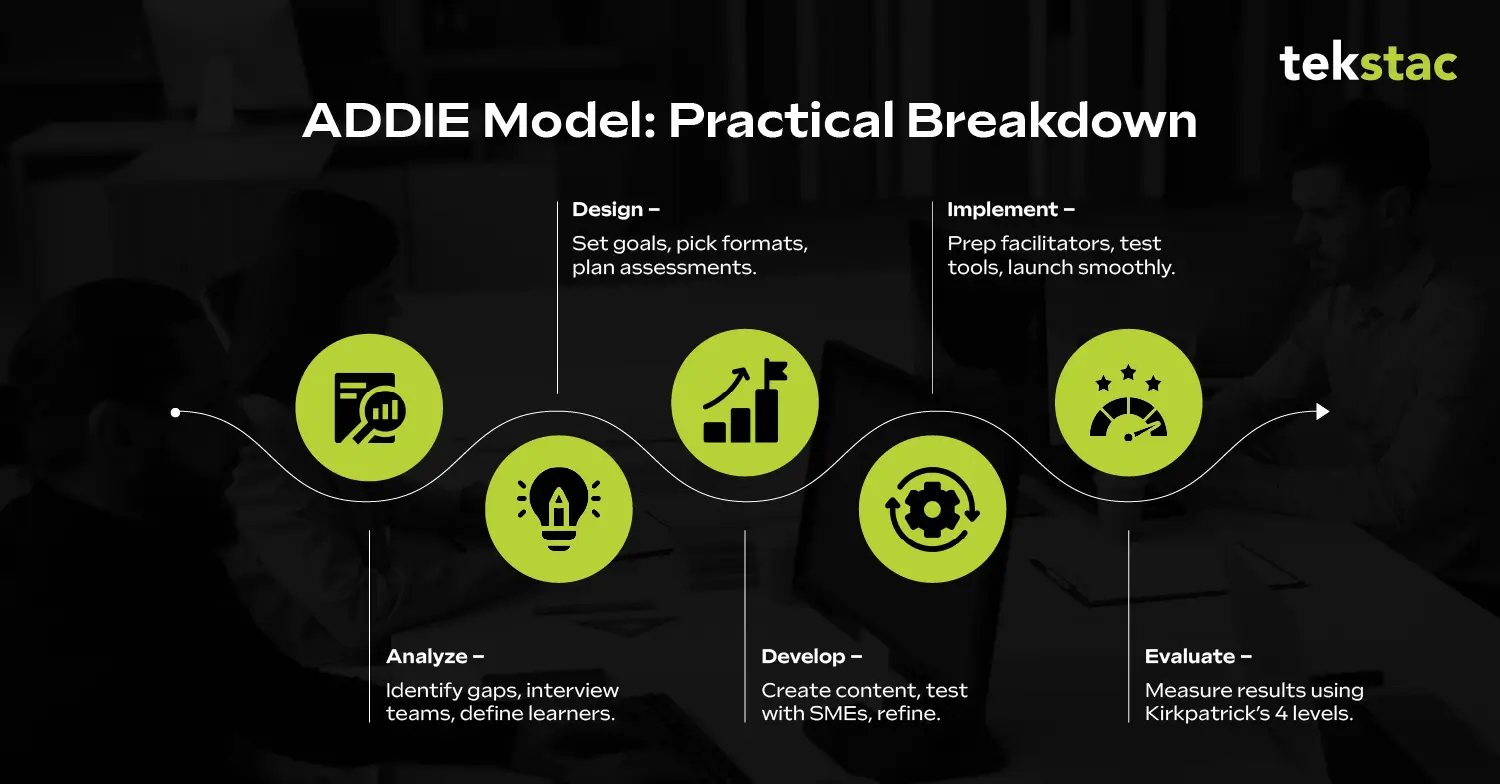
The ADDIE model is a five-step phase for designing and implementing learning programs. It is an acronym for Analyze, Design, Develop, Implement, and Evaluate, representing five unique phases that walk you through from recognizing a learning need to measuring its business consequence.
The World Economic Forum reckons that 40% of the most important skills needed in the labour market will shift because of AI, automation, and evolving job roles by 2030. Meanwhile, L&D budgets are increasing, as 85% of employers intend to implement upskilling approaches between 2026–2030. This goes on to explain that organizations are betting heavily on talent development but require established, systematic models such as ADDIE that ensure desired results.
ADDIE Model Framework: Phase-by-Phase Breakdown
In the ADDIE model, each step forms the building block for the subsequent step, making a pathway from business needs identification to the delivery of effective learning solutions.
Make sure not to skip any stage, as the whole process gets compromised. For instance, if you don’t examine the correct problem, your training and development program will be off the target, and you will end up with training that fails to address performance gaps. This also results in wasted resources, unmotivated learners, and no measurable effect. Any workforce upskilling method must follow a structured approach to be effective.
Here’s a practical phase-by-phase ADDIE model breakdown so you can implement practically:
Phase 1: Analyze – Identifying Skill & Performance Gaps
Before you build anything, you need to know what business problem your learning program is solving. The Analyze phase anchors your learning intervention to a real-world business problem. It pinpoints the exact performance gap your employees face and why it exists. In other words, you’re diagnosing a business problem that learning might help fix.
In most organizations, performance gaps show up subtly. Whatever the case, the problem is always reflected in business metrics: attrition, ramp-up time, NPS, conversion, quality scores, and so on. This phase helps you trace those symptoms to specific skills, behaviors, or knowledge gaps.
Start with the business problem: The first step is identifying the problem. This step aims to understand why performance is lagging and whether a learning intervention is the right response. The more straightforward your diagnosis, the more focused and effective your solution will be.
- Review recent business KPIs to spot underperformance
- Identify departments or teams where output has dipped or errors have increased
- Interview managers to surface recurring workflow or behavioral issues
- Map any recent process, policy, or structural changes that may have caused confusion
- Write a 1-2 sentence problem statement defining the gap
Talk to stakeholders: Interview stakeholders, such as managers, high performers, underperformers, and cross-functional teams to identify the challenges and behaviors that are causing the issue.
- Interview managers and employees across levels
- Ask where people struggle most and what behaviors impact success
- Explore recent tool, process, or team changes causing friction
- Identify what people currently do to solve challenges, and what’s missing
Understand who you’re designing for: Consider your audience’s real work context. Consider their roles, daily challenges, tools, and learning preferences. Create a simple learner profile that highlights their pain points and blockers.
According to Deloitte, companies that follow structured learning models like ADDIE are 3.6x more likely to report measurable improvements in employee performance.
Phase 2: Design – Mapping Learning Objectives to KPIs
This stage transforms the findings gathered in Phase 1 into a roadmap that directs the creation of training and development materials. The intention here is to develop an elaborate map that links learning outcomes to changes in behavior and measurable business outcomes. Prepare yourself for providing answers to questions such as:
- What specific learning objectives will close the performance gap?
- Which instructional strategies and formats will engage your learners?
- How will you sequence the content for maximum impact?
- What assessment methods will confirm learners are applying new skills effectively?
Define clear learning objectives: Start by crafting your business problem into well-articulated, measurable learning goals. These need to be precise, actionable, and geared toward behavior or skills that have a direct influence on performance.
- Write objectives that answer: “What should learners be able to do differently after training?”
- Use action verbs (e.g., demonstrate, apply, analyze) to ensure clarity
- Align objectives with the desired business outcome defined in Phase 1
Choose the right learning strategies and formats: Select instructional methods that fit the audience’s preferences, context, and learning goals. Look at microlearning strategies, application based learning, workshops, simulations, or blending learning. Consider accessibility, time constraints, and resource availability. Make sure to sequence learning to progress smoothly from foundational knowledge to mastery along with practical applications.
Plan assessment and success metrics: Design formative assessments to reinforce learning during the program and plan summative assessments to validate skill adoption at the end. Ensure to align assessment criteria with business success metrics established earlier.
Phase 3: Develop – Building Learning Content and Assessments
The development phase is where your learning solution comes to life. In this production stage, you create and assemble all training materials. This demands collaboration to ensure content quality, relevance, and consistency with learning objectives. It’s also the time to integrate tools and technology that will help deliver the program smoothly. Build drafts, test them internally, gather feedback, and refine them before launch. This cycle helps catch gaps early.
- Ensure every material directly supports your defined objectives and reflects real learner challenges
- Engage subject-matter experts early on to review and validate the quality and applicability of your content
- Add examples and anecdotes that connect with learners’ everyday activities
- Plan frequent check-ins and leverage collaborative tools to track versions, feedback, and approvals easily
- Run soft launches, collect structured feedback through surveys or interviews, and refine content
Phase 4: Implement – Delivering the Training Program
After your learning materials are refined and approved, it’s time to implement the learning program in real life. This step guarantees the training launch is smooth and that learners can interact optimally. Therefore, it calls for extensive planning and coordination to prevent glitches
Prepare trainers and facilitators: Provide thorough briefings, detailed facilitator guides, and rehearsals if needed.
Set up the learning environment: Ensure that your LMS, virtual classroom, or physical space is fully prepared before launch. Test all technical elements, including access, multimedia playback, and interactive tools. Confirm that learners have the right permissions and resources.
Communicate early with learners: Share program objectives, schedules, and how learners can access materials or sessions. Provide clear instructions and support contacts for any technical or content questions.
Phase 5: Evaluate – Measuring Learning Impact and ROI
Evaluation is the vital last step in the ADDIE model, where you compare the success of your learning program against initial objectives. This step makes sure you are aware of the influence on the learner performance as well as the larger business goals. Without evaluation, all your work may be wasted or incorrect.
You need to assess whether learners have acquired the intended skills or knowledge and, more importantly, if their behavior or performance has improved on the job. This data guides future iterations and helps justify training investments. Use a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to gather comprehensive insights. Look beyond immediate reactions and track long-term changes wherever possible.
Focus on multiple levels of evaluation: Kirkpatrick’s model is a proven framework here:
- Level 1: Reaction: Did learners find the training relevant and engaging?
- Level 2: Learning: Did they absorb the content and develop the skills?
- Level 3: Behavior: Are they applying what they learned on the job?
- Level 4: Results: Is the business seeing measurable improvements tied to training?
Collect data methodically: Use surveys, quizzes, interviews, performance metrics, and observation to collect data. Evaluate at multiple points, such as immediately post-training, 30 days after, and ideally after 90 days to track sustained impact.
Keep in mind that Phase 5 is not a one-time activity. Use your findings to identify gaps, refine content, enhance delivery, and scale successful elements.
ADDIE Model Case Study: How IBM Transformed Leadership Talent
Here is one company that successfully implemented the ADDIE model for talent development:
IBM
In the late 1990s, IBM felt a vanishing sense of leadership readiness. The business diversified across borders and business units, yet first-line managers were unprepared. The transition from individual contributor to leader was shaky, and managers lacked a shared understanding of good leadership. That’s when IBM rolled up its sleeves and brought in an old and sharp framework, the ADDIE model, turning it into its own Basic Blue training program. The fourth tier of the program was defined as the Evaluation phase of ADDIE.
Analyze: IBM recognized that first-line managers were unprepared for leadership roles. Too often, they emerged from individual contributor roles lacking key managerial skills. Their audit revealed critical gaps in delegation, feedback, and team management.
Design: IBM designed Basic Blue as a 4-tier e-learning blended program, with three online tiers being articles, simulations, and job aids. This was followed by a final in-person “Learning Lab” classroom session.
Develop: IBM produced multimedia-rich content, Manager QuickViews (editable Q&A databases), and simulations.
Implement: Basic Blue was delivered globally. First, online tiers were completed, followed by a week-long classroom experience. Completing digital tiers was mandatory before attending the Learning Lab.
Evaluate: IBM measured performance impact by identifying outcomes like better team management.
Ultimately, based on its early deployment, IBM achieved an ROI of 2,284% in 2001. After launching Basic Blue in 2000, IBM also generated $16 million in savings, and broader e‑learning programs saved $200 million that same year.
How to Embed the ADDIE Model into Your Talent Development Strategy
At the heart of every successful talent development strategy lies one core truth: structure. Just like IBM followed a clear, methodical framework when designing its Basic Blue program, every organization must begin with a solid foundation. This involves identifying skill gaps, structuring focused learning interventions, and ultimately putting in place mechanisms for monitoring and measuring impact.
Having a proper system, like Tekstac, is essential for L&D teams, especially those managing tech teams. Leading enterprises like IBM, PwC, and Accenture have embraced Tekstac to add more content and build repeatable, scalable, and trackable capability-building programs.
With the features below, Tekstac empowers HR and L&D teams to run talent development initiatives confidently at scale.
- Real-time skill gap analytics
- Immersive, hands-on labs
- Automated assessments
- Detailed progress tracking
Ready to apply the ADDIE Model to your organization? See how Tekstac helps design, deliver, and measure talent development programs with real ROI. → Book a demo
FAQs on ADDIE Model
1. What are the five phases of the ADDIE Model?
The ADDIE Model includes five structured phases: Analyze, Design, Develop, Implement, and Evaluate — used to build effective learning programs.
2. How does the ADDIE Model compare to the SAM Model?
ADDIE is linear and structured, while SAM (Successive Approximation Model) is iterative and rapid. ADDIE suits large, complex talent programs; SAM suits fast prototypes and agile learning needs.
3. Can the ADDIE Model be automated with learning technology?
Yes. Platforms like Tekstac automate skill gap analysis, learning path creation, hands-on assessments, and performance metrics — accelerating ADDIE-based learning programs at scale.
4. How does the ADDIE Model support talent development?
ADDIE aligns learning programs with business goals by diagnosing skill gaps, designing targeted training, and measuring improvement in on-the-job performance.
How to Measure the ROI of Employee Training Programs
Companies are investing more than ever in employee learning and development. Yet, for many HR and L&D teams, answering a basic question remains frustrating, “Is it working?”
Despite billions of dollars spent on upskilling and training each year, 61% of training leaders still do not measure the ROI of their training programs. Even when employee training outcomes are measured, they’re often reduced to surface-level metrics, such as completion rates, smiley-face surveys, or test scores. While these are useful, they are neither sufficient nor adequate.
Many organizations cite lack of clear goals, insufficient resources, and uncertainty about where to start as the top challenges in measuring training ROI.
7 Steps to Measure the ROI of Employee Training Programs
Let’s take a realistic approach and a practical step-by-step process that covers actual training costs, integration with business goals, and how to use the data you already have.
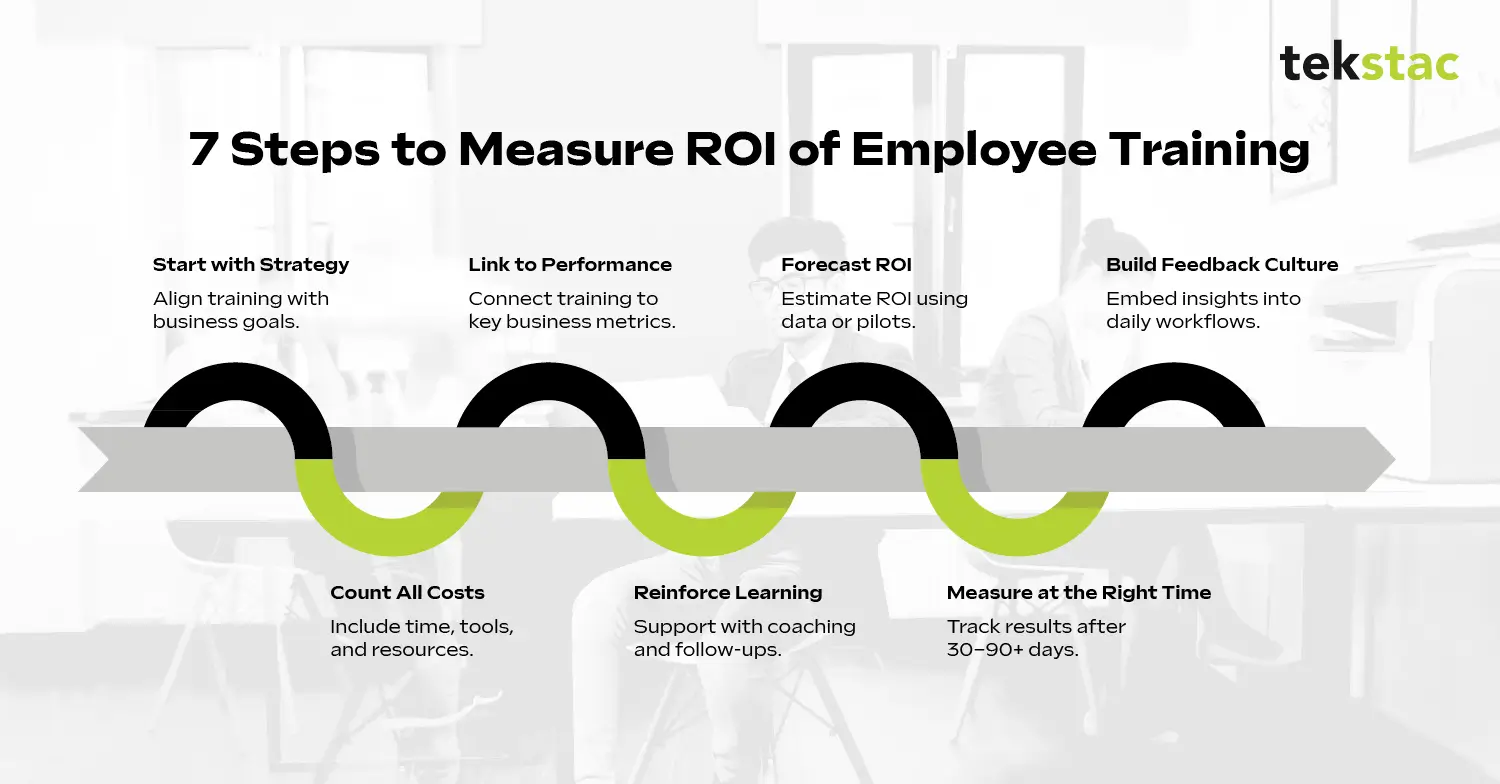
1. Start with strategic intent, not skill gaps
Most organizations begin their workplace training by identifying skill gaps, those missing competencies or technical skills employees lack. Focusing solely on skill gaps is a limited view that misses alignment with the company’s broader strategic goals and outcomes.
If L&D efforts fail to connect to what the business is trying to achieve, measuring learning impact becomes ineffective. Hence, without this strategic intent, most organizations fall prey to measuring ineffective ROI metrics like course completions or quiz scores but not outcomes such as increased revenue, improved customer satisfaction, faster product launches, etc.
To do this practically, begin every training program with a conversation beyond HR or L&D. Bring in stakeholders from business units, operations, sales, and leadership. Ask questions like:
- What are our top three business challenges this quarter or year?
- What behaviors or capabilities need to shift to meet those challenges?
- How will we know if those shifts happen?
From there, create learning objectives that tie directly to these priorities. This sets the foundation for meaningful ROI measurement. Determining learning success through business KPIs rather than just learning KPIs allows you to identify the right metrics upfront.
For example, instead of “improve negotiation skills,” a strategic intent might be to “reduce average sales cycle time by 15% through improved negotiation.”
2. Calculate the actual cost of training
Training budgets are generally calculated based on platform licenses, facilitator fees, or travel expenses. However, this approach does not capture the full cost of ownership of workplace training programs. Here’s how to ensure a more accurate cost baseline:
Employee time: Every hour spent in training is not spent on other productive work. This opportunity costs scales quickly across large cohorts.
Manager involvement: This includes conducting follow-ups, assigning pre-work, or leading on-the-job practice sessions, as they dedicate time and energy that needs to be accounted for.
Post-training reinforcement: Job aids, nudges, simulations, or coaching continues long after completing a course.
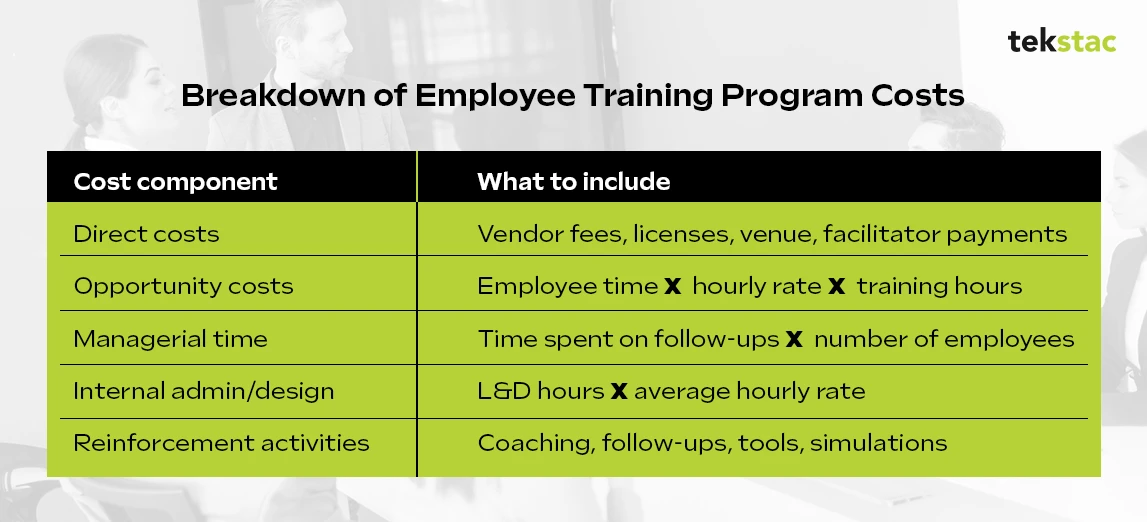
Many companies hesitate to investigate these costs out of fear they’ll seem too high, but being honest about the real cost of training actually strengthens credibility when showing impact, as leaders need an accurate number rather than a lower one.
3. Integrate training metrics with performance data
Connect training outcomes with relevant performance data, sales figures, error reduction, customer satisfaction scores, or productivity rates. Start by identifying which business metrics your training will influence, then collaborate with data owners in departments like sales, customer success, or operations. They often track these metrics regularly and can provide historical data for comparison.
Now, create a simple data dashboard or report that overlays training participation data with these business KPIs over time. Look for patterns like improvements in key metrics following the training rollout—segment data by employee groups who took the training versus those who didn’t to isolate the impact.
For example, if average sales increase by 10% post-training in your trained group compared to untrained peers, that’s a clear signal of positive ROI. You can then translate that uplift into dollar values for your ROI formula.
4. Reinforce training or watch it decay
Some employee training programs fail because of what happens after the session ends. Per the Forgetting Curve concept, 90% of learning is forgotten within a week if not reinforced. As we observe, most L&D programs still operate on a “one-and-done” model.
Training is not a single event; it’s a process of behavioral change. Without reinforcement, there’s no lasting change, hence no real ROI. This means measuring training ROI must include structured reinforcement. Here’s what to include:
- Manager-led debriefs
- Microlearning nudges
- Job aids and checklists
- Peer sharing sessions
- Follow-up assessments
Tip: When planning your program, allocate at least 20-30% of your training budget or timeline to reinforcement.
A simple way to measure ROI with reinforcement in place would be to use this formula:
ROI of training programs (%) = (Total Benefit – Total Cost)/Total Cost x 100
Let’s break this down:
Total benefit = Business gains because of the training (e.g., time saved, revenue increased, increase in resolution times, etc.)
Total cost = Training costs + time + reinforcement tools or coaching
5. Predict ROI
Predicting ROI upfront helps align expectations and secure stakeholder buy-in. Many organizations skip this step, making it harder to justify investments or set realistic goals. You can estimate the potential business impact your training can have based on historical data, benchmarks, or pilot programs. Forecast the costs involved so you have a clear picture of the investment
Predicted ROI (%) = (Expected Benefit – Cost)/Cost x 100
You can use smaller pilot groups to test training impact quickly before wider rollout and gather early performance signals, like knowledge application or behavior change, to adjust predictions. While predictive ROI isn’t perfect, it sets a proactive foundation for tracking and optimizing training success.
6. Time your ROI measurement
Measuring ROI too soon can be the biggest trap. True business impact from training often takes time to materialize. Behavior changes, productivity gains, or revenue improvements rarely appear overnight. It’s important to recognize that a training program might initially show a negative ROI or no measurable benefit—not because it failed, but because you haven’t yet reached the break-even point where benefits outweigh costs. To measure employee training ROI right:
- Set realistic evaluation windows (30,60,90 days or 6 months) based on training type.
- Assess learner engagement, knowledge retention, and behavior changes soon after training.
- Measure key business outcomes like sales performance, error rates, or customer satisfaction over a longer period.
- Regularly assess ROI to track progress over time and capture delayed benefits.
If, after the appropriate measurement window, ROI remains negative, don’t see it as a failure but as a sign to dig deeper. It could mean the training wasn’t aligned with business priorities, the delivery method ineffective, or the benefits are harder to quantify. Use this insight to reassess training goals, refine the training content, improve reinforcement strategies, or adjust your metrics.
7. Embed cultural insight and continuous feedback for sustainable ROI
Training effectiveness depends heavily on how well it aligns with organizational culture, leadership support, and employee readiness to change. If the culture resists new behaviors or lacks reinforcement mechanisms, ROI will suffer despite great content or delivery. Factors like peer influence, manager involvement, and workplace norms shape whether learning turns into performance improvements.
Create channels to collect feedback not only immediately after training but throughout the learning journey. This includes:
- Regular pulse surveys on behavior change
- Manager check-ins for skill application
- Performance data reviews to spot trends and gaps
- Open forums or focus groups for qualitative insights
The key here is to partner with managers to embed learning checkpoints into regular workflows, leverage technology platforms that allow real-time feedback and data integration, and communicating changes periodically.
Want practical strategies and future trends in employee development?
👉 Explore more in our full blog.
Next training program coming up? Time to lock in the ROI
To actually measure training impact, the preparation work starts much earlier, with how you design your training ecosystem. There’s a need for a tool that not only delivers content but effectively tracks, connects, and analyzes every learning touchpoint against actual business KPIs.
Tekstac’s learning analytics and management modules help perfectly:
- Leverage custom dashboards with real-time progress tracking and KPI overlays
- Anticipate outcomes before full rollout with our predictive analytics
- Track every input and output with talent supply chain view
- Align skilling with future business needs with skill inventory monitoring
- Simplify insights for business leaders with custom reports
The platform also powers your learning experience with custom learning paths, mentor marketplace, virtual sessions, auto-evaluated practice labs, AI-proctored assessments, and many more. With over 1 million professionals upskilled, 24 million+ learning hours, and enterprise customers like IBM, PwC, Capgemini, and Cognizant, Tekstac is built for organizations that want to transform how they train and upskill. See Tekstac in action.
How to Integrate AI and Automation in Talent Development Programs
The world of work isn’t just changing; it’s evolving faster than most companies can keep up. What used to work ten years ago, scheduled training sessions, fixed job descriptions, manual performance reviews, is now dangerously outdated.
In this environment, a business is only as strong as the adaptability of its people.
Why Traditional Talent Development Programs Are No Longer Enough
This is where Talent Development Programs come into the picture. These aren’t just employee workshops or onboarding checklists anymore. They are enterprise engines.
Engines that build skill, enhance judgement, and turn employees into contributors capable of facing the unknown with confidence.
According to a 2025 McKinsey report, 60% of executives now say their company’s competitive edge depends on how quickly they can reskill their people.
That’s not HR fluff.
That’s a strategic priority for business growth.
And yet, most organizations are still treating talent development like a cost center, not the profit multiplier it actually is.
The real problem is that training is still reactive. It’s not aligned to the job. It’s not intelligent. And in many cases, it’s not even reaching the right people at the right time.
That’s why businesses lose talent, productivity, and in the long run, relevance.
What Smart Talent Development Programs Unlock
There’s a better way. One that treats talent like a living system, not a static resource. The new standard for Talent Development Programs is adaptability.
Not just what employees know, but how quickly they can learn something new when the rules change.
This is where AI in learning and development becomes mission-critical. AI/ML based HRTech tools now enable companies to tailor learning paths for each individual, not just based on their role, but on performance patterns, their career aspirations, business requirements, learning style, and growth trajectory.
Take a look at what this unlocks
- Personalized learning delivered at the moment of need
- Real-time skill gaps analysis
- Auto-curated content libraries based on job performance
- Virtual mentors that provide 24/7 feedback and coaching
In a recent LinkedIn Workplace Learning report, companies that invested in AI-enabled talent development platforms reported a 23% increase in internal mobility and a 30% reduction in turnover.
That’s how powerful smart development can be.
And don’t ignore Upskilling through automation. When machines handle repetitive tasks, human workers must step into higher-order thinking roles, negotiation, decision-making, leadership. But they can only do that if they have the necessary skills.
How Leading Companies Are Transforming Talent Development
Let’s break this down through a practical lens.
Unilever, one of the world’s top consumer brands, completely reshaped its approach to talent development by dismantling traditional roles and replacing them with task-based assessments.
Instead of promoting based on time served, employees were assessed based on project complexity, agility, and learning speed.
With AI embedded in its learning system, Unilever enabled every employee to build their own career map, automatically updated based on skill growth and business needs.
This shift didn’t just improve retention, it unlocked hidden talent across the entire organization.
Or consider Genpact, a global services company. When GenAI exploded onto the scene, they immediately created AI-driven employee development tracks focused on prompt engineering and LLM literacy.
Over 75,000 employees completed their AI foundation module in under 6 months, leading to a 3x increase in total learning hours over the past four years.
These aren’t edge cases. They’re the new standard.
The Pillars of Future-Ready Talent Development Programs
Now here’s what every business needs to start doing immediately
1. Build Learning into the Flow of Work
People won’t engage in training if it interrupts their work. That’s why modern Talent Development Programs embed learning into tools already being used — Slack, Teams, project management software. Microlearning modules triggered by real work tasks.
No separate login.
No off-site seminar.
2. Use AI to Deliver Just-in-Time Feedback
Learning must happen when it matters most. With AI in learning and development, systems can now evaluate an employee’s real-time performance, detect errors or gaps, and offer corrective content instantly.
No need to wait for the next quarterly review.
3. Make Reskilling a Default, Not a Perk
A 2025 World Economic Forum study found that over 40% of all workers will need reskilling within the next three years.
That means Upskilling through automation isn’t a nice-to-have. It’s a survival plan. Companies must fund, incentivize, and promote reskilling pathways by default.
4. Shift Focus from Degrees to Skills
Credentials are no longer the main currency of value. The ability to adapt, learn, and apply new knowledge rapidly is what counts. AI systems can assess these traits better than any traditional resume scan.
A recent SAP SuccessFactors case study showed that companies adopting skill-first development models saw a 26% increase in project delivery speed and a 15% improvement in leadership pipeline efficiency.
5. Map Development to Business Strategy
This is where too many get it wrong. Learning is treated as an HR metric, not a revenue enabler. True AI-driven employee development maps every learning track to a clear business objective — cost reduction, faster innovation, customer satisfaction, leadership capacity. Training must be an investment that pays back.
The Strategic Business Advantage of Modern Talent Development
Every company is sitting on a goldmine. Their people. But talent without development is just potential, not performance. The companies that win in this next decade won’t be the ones with the most capital, but the ones with the most adaptable workforce.
Talent Development Programs are no longer optional. They are the core infrastructure. As critical as cloud servers or cybersecurity. And when powered by AI, they don’t just train workers. They evolve them.
The time to act is now. The longer the delay, the wider the skills gap becomes.
And here’s the truth. Implementing this doesn’t have to be hard. Not with the right partner. There are platforms today that can deploy these capabilities out of the box — from smart learning paths to performance-linked coaching to skill analytics that make HR feel like strategy.
How AI Is Driving the Next Phase of Talent Development
It’s a different game now.
Static roles have been replaced by skill clusters. One-size-fits-all training is obsolete.
And AI isn’t just automating tasks — it’s building talent.
There’s no turning back. The choice for organizations is simple.
Keep relying on outdated training systems, lose people, fall behind.
Or, switch to intelligent, data-driven, personalized development and build a workforce ready for anything.
Unlock the Future of AI-Driven Talent Development
If there’s one place to start, it’s with a smart platform that aligns learning, performance, and business goals.
One that offers everything from skill taxonomies to AI-powered coaching, from role-based content curation to real-time feedback — all personalized, scalable, and integrated
Try Tekstac today and experience what intelligent talent growth can really look like
👉Get Started Now
FAQs on Talent Development Programs
1. What are the key benefits of AI-powered talent development platforms?
AI-powered platforms improve internal mobility, reduce turnover, accelerate reskilling, and provide data-driven insights into workforce readiness. They help organizations build future-ready talent while turning learning investments into measurable business impact.
2. How does AI improve learning and development programs?
AI improves learning and development by delivering personalized, just-in-time content, automating skill assessments, and providing real-time feedback. It helps organizations scale training efficiently while increasing engagement, retention, and measurable performance outcomes.
3. How does AI-driven talent development support business growth?
AI-driven talent development aligns employee skills with strategic objectives such as innovation, operational efficiency, and leadership readiness. By reducing skill gaps and improving workforce agility, companies achieve faster execution, better retention, and long-term competitive advantages.
4. What business outcomes can talent development solutions deliver?
Talent development solutions improve productivity, accelerate time-to-skill, strengthen leadership pipelines, reduce hiring costs, and support faster innovation by aligning workforce capabilities with strategic business priorities.
7 Proven Workforce Development Strategies to Implement in 2026
Why Most Workforce Development Strategies Fail in 2026
If more than 90% of employees say they’d stay longer at a company that invests in their career, why are so many still leaving?
The answer is simple. Most workforce development strategies are not working. They’re well-intentioned, but too generic, reactive, or completely disconnected from what employees need to grow—and what the business needs.
Organizations are spending time and money on learning initiatives. Over half of them list upskilling and reskilling as a top priority. However, only 21% believe their efforts are practical. While this internal pressure causes misalignment, external pressure is mounting.
With AI and automation expected to disrupt nearly half of all jobs in the coming years, most organizations still lack access to the right resources.
This is the gap companies need to close, and in this blog, we’ll discuss exactly how, with the most effective employee upskilling strategies.
What Makes a Good Workforce Development Strategy?
If we look at the root cause of most ineffective workforce development strategies, we find they’re performative. A few courses here, a new platform there, perhaps some annual compliance training—they rarely drive any change on the ground.
According to the LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report, 94% of employees would stay longer at a company that invests in career development — yet most organizations still struggle to offer structured, measurable workforce development.
In 2026, a good workforce development strategy is built with intention. Let’s see how.

1. It’s centered on future skills, not just “more” skills
Just because employees are learning something doesn’t mean it’s moving the needle. A solid strategy focuses on the adoption and practical use of future-forward skills. The goal isn’t to train for training’s sake. It’s to ensure your workforce is equipped for the shifts across your industry.
2. It prioritizes purposeful, personalized learning
Throwing generic content at employees and hoping it sticks is not a strategy. A meaningful employee upskilling strategy personalizes learning to the employee’s role, growth path, and learning style, while ensuring every resource serves a clear purpose. Whether self-paced modules, peer mentoring, or live sessions, every touchpoint should move the learner (and the business) forward.
3. It connects directly to business outcomes
Learning in isolation won’t drive results. The strongest strategies are mapped directly to business goals: increasing customer satisfaction, enabling digital transformation, or closing leadership gaps.
As always, a good employee development strategy must be measurable. If you can’t track skill development, impact, and progress, you’re just guessing. Additionally, development shouldn’t be a separate activity employees do when they “find the time.” The best strategies are embedded into everyday workflows through feedback, real projects, coaching, and collaboration.
7 Proven Workforce Development Strategies for 2026 and Beyond
As we often notice, some development strategies die quietly after a while, even after allocating training budgets or launching an LMS. If you’re wondering why nothing’s changing on the floor or if you want to take a more innovative approach to workforce development, below are the top 7 workforce development strategies.
1. Future-Back Skill Planning
If your workforce development strategy starts with you looking at current roles and asking, “What’s missing?” you’re already going backward. The smarter question is, “What roles and skills will we need in two years—and how do we build for that now?” Future-back skill planning starts with forecasting future capabilities based on business goals, market shifts, and industry evolution. It requires a partnership between HR, L&D, and leadership to identify skill adjacencies, define learning paths, and bake them into career journeys.
2. Build Company-Wide AI Literacy
With the rise of AI, most companies are excited to invest in GenAI or piloting chatbots. However, employees may still be unaware how exactly it embeds into their work. For example, does your payroll team know how AI affects them? Does your customer service team understand how it’ll change how they work?
AI literacy can’t be just for the IT crowd or the early adopters. Everyone in your company needs to know what AI means for their job — what it automates, what it makes easier, and what it demands from them now.
3. Create Personalized Learning Funnels
Most learning strategies assume people are all starting from the same point, learning in the same way, and aiming for the same goal. This usually ends up in choosing a same course or a learning platform that leave high performers bored and struggling folks overwhelmed.
A better approach would be to build learning journeys like real paths based on where someone actually is, rather than assuming where the employee stands, knows, or wants to go.
4. Make Career Growth Predictable
Ask people how to grow in their company, and most will shrug. Very few know what leads to a promotion or a role switch. This is a big problem. Career paths are usually vague, unspoken, or left to chance. And when there’s no clarity, the same types of people keep getting promoted while others get stuck.
Make growth feel intentional. Start by mapping out what success looks like in each role. Be specific. What skills, outcomes, and behaviors are needed to level up? Don’t keep it locked in a PDF either, bring it into everyday conversations. Managers should reference these paths in check-ins.
5. Use Immersive Learning to Close the Practice Gap
Some traditional L&D strategies run like a school timetable, involving annual plans, quarterly workshops, and calendars. But work doesn’t wait for Q3 to teach you something. It throws new tools, priorities, and challenges at you out of nowhere. When learning doesn’t show up in those moments, people either wing it or stall.
A better way would be to make learning immediate by using microlearning. If someone’s stepping into a new project, give them a quick how-to guide right then. Learning has to move at the speed of change. Otherwise, it’s already too late.
6. Measure Whether People Got Better
Solely looking at whether the employee has completed the course doesn’t help determine if they learned anything. Hence, measure impact. If someone took a negotiation course, are they actually closing deals better? If they were trained on giving feedback, is their team communicating more clearly? Tie learning to actual outcomes — better performance, fewer errors, stronger collaboration.
7. Make Development a Shared Ownership
As we often notice, workforce development gets boxed into L&D or HR. However, real growth happens in the flow of work, driven by managers, shaped by teams, owned by employees. That shift only happens when everyone sees development as their job. Give employees visibility into skill paths. Equip managers to enable growth, not just review it. And get leaders to invest in learning as a lever for business impact. Ultimately, when employee development becomes a shared ownership, it scales.
Empowering Managers to Focus on Strategic Leadership
In many organizations, managers are expected to drive both project outcomes and team development. However, without the right tools, they often struggle to provide consistent, personalized growth opportunities for their teams. This gap can lead to disengagement and high turnover.
The right tools, like Tekstac, address this challenge by offering an AI-powered, end-to-end skilling platform that automates and personalizes the learning journey for each employee.
What Makes Tekstac Different for Workforce Skill Development
With over 500+ curated learning paths covering in-demand tech areas like data analytics, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, Tekstac ensures that employees have access to relevant, up-to-date content.
The platform’s integrated lab environment enables real-time, hands-on practice across various technologies, allowing employees to apply new skills in a controlled setting. Additionally, AI-driven personalization analyzes skill assessments to identify knowledge gaps and recommends tailored learning paths aligned with individual career goals.
Built-In Insights for Managers and L&D Teams
Tekstac provides real-time insights into team progress through intuitive dashboards and analytics. This visibility allows managers to track development, plan interventions, and make informed decisions without micromanaging the learning process.
Ultimately, managers and organizations can focus on strategic leadership and team engagement, confident that their teams are progressing along personalized, goal-oriented learning paths.
Want to apply these workforce development strategies inside your organization? Book a free strategy consultation with our L&D experts.
FAQs on Workforce Development Strategies
1. How do I create a workforce development plan?
Create a workforce development plan by assessing current skills, identifying future skill needs, building training paths to close gaps, assigning ownership, and tracking progress with measurable outcomes.
2. What are the most effective global workforce development strategies?
The most effective global strategies emphasize continuous learning, skills-based career paths, digital skilling, remote-friendly learning platforms, and culturally adaptable training content that support diverse teams.
3. How do you measure the success of workforce development?
Success is measured using KPIs like skill assessments, project outcomes, goal achievement, time-to-productivity, promotion rates, and employee engagement.
How Tekstac Skills Assessments Improve Learning Outcomes and Drive ROI
“If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it.” This simple truth is the foundation of modern learning and development strategies. As organizations channel time, effort, and resources into upskilling and reskilling their people, the focus has decisively shifted from activity to impact. It is no longer enough to know that a course was completed, or a training was attended; stakeholders want to understand what the learner gained. This is where Learning Outcomes come into play.
What Are Learning Outcomes? Definition & Importance
Learning outcomes are the specific skills, knowledge, attitudes, and competencies that a learner is expected to acquire as a result of a learning experience. Unlike learning objectives, which describe what the instructor aims to teach, learning outcomes describe what the learner can do after the training. These outcomes are measurable and actionable, making them essential for evaluating learning effectiveness.
Examples of learning outcomes include:
- A marketing executive being able to analyze customer segmentation data.
- A programmer demonstrating secure coding practices.
- A manager applying emotional intelligence in team interactions.
Why Measuring Learning Outcomes Matters for Organizations
Organizations invest millions in learning and development each year. But without concrete measurement, these initiatives risk becoming superficial. Here are some key reasons why measuring learning outcomes is critical:
1. Validates Learning Effectiveness
Measuring outcomes helps determine whether a training initiative led to improved skills or behavior change. This validation ensures that learning is meaningful, not just procedural.
2. Enables Personalization and Continuous Improvement
Assessment of learning outcomes helps identify skill gaps, enabling personalized learning paths. For instance, if a learner struggles with a certain concept, targeted content or support can be introduced. Over time, this leads to continuous improvement in both learning content and learner performance.
3. Aligns Learning with Business Goals
When learning outcomes are tied to business objectives (like improved customer satisfaction, increased productivity, or reduced error rates), it creates alignment between individual development and organizational success.
4. Drives Accountability
In today’s data-driven world, L&D departments are increasingly accountable for delivering measurable results. Outcomes-based measurement offers transparency and builds credibility with stakeholders.
5. Informs ROI Calculations
You can’t demonstrate ROI without data. Measuring learning outcomes provides the metrics needed to correlate learning interventions with business impact, making it possible to justify or even expand the L&D budget.
The Shift Toward Data-Driven Learning Outcomes Measurement
Traditional learning measurement methods, such as tracking attendance and course completion, are giving way to more sophisticated, data-rich approaches. Organizations now leverage data analytics to capture granular insights into learner performance, progression, and engagement.
This shift is fueled by the increasing availability of digital learning platforms and AI-driven tools that collect, process, and analyze learning behavior in real-time. Predictive analytics, adaptive assessments, and learning experience platforms (LXPs) are transforming how we measure success. By using data to continuously evaluate and refine learning interventions, organizations ensure that every learning dollar is spent strategically.
According to a Deloitte survey, 61% of high-performing organizations use data analytics to support learning strategy development- more than double the rate of their lower-performing peers.
How Learning Outcomes Connect to Business ROI
The ultimate goal of measuring learning outcomes is to prove—and improve—return on investment (ROI). Here’s how outcomes data directly impacts ROI:
1. Demonstrating Business Impact
Clear outcomes link learning efforts to key business metrics such as employee performance, customer satisfaction, and innovation speed. For example, improved sales training outcomes can be measured against increased revenue or shorter sales cycles.
2. Optimizing Training Spend
Outcome data helps identify high- and low-performing programs, enabling better budget allocation. By cutting ineffective initiatives and scaling successful ones, organizations maximize learning ROI.
3. Supporting Workforce Planning
By measuring outcomes, organizations can identify future leaders, skill shortages, and team strengths. This enables proactive talent management and succession planning.
4. Reducing Time-to-Competency
Effective training backed by measurable outcomes shortens the time it takes for employees to reach full productivity, accelerating ROI.
5. Boosting Employee Retention and Engagement
Employees who see real career progression through skill development are more engaged and less likely to leave, significantly reducing attrition costs.
Modern Methods to Measure Learning Outcomes Effectively
Many organizations still rely on traditional methods like attendance tracking, course completion rates, or post-training feedback forms. While useful for gauging engagement or satisfaction, these methods do not assess skill application or knowledge retention.
Modern approaches include:
- Formative and summative assessments: Conducted before, during, and after learning to evaluate comprehension.
- Simulation-based assessments: Providing real-world scenarios to test applied skills.
- Project-based evaluations: Where learners are required to submit real or simulated work relevant to their job roles.
- 360-degree feedback and peer assessments: Offering a more holistic view of behavioral and performance outcomes.
- AI-driven analytics: Delivering personalized insights into learner strengths and gaps.
The Business Impact of Learning Outcomes Measurement
1. Improved Decision-Making
When you have clear data on what works and what doesn’t, you can make better decisions about content, delivery methods, and resource allocation.
2. Better Learner Engagement
Learners who see a direct link between their efforts and career growth are more motivated. Measurable outcomes act as milestones that validate progress.
A McKinsey study reveals that only 40% of companies align learning strategies with business objectives, underscoring the need for clearer measurement frameworks that connect learning outcomes to performance and ROI.
3. Stronger Organizational Performance
A Harvard Business Review report shows that companies that effectively measure and act on learning data are 24% more profitable than their peers.
4. Increased Adaptability
In a fast-changing market, the ability to rapidly upskill or reskill talent is a competitive advantage. Measuring learning outcomes helps build this agility.
5. Justified Investments
According to a LinkedIn Learning report, 73% of L&D professionals say their leadership wants them to connect learning to business outcomes. Accurate measurement makes this possible.
Key Challenges in Measuring Learning Outcomes Accurately
Despite its importance, outcome-based measurement is not without challenges:
- Lack of standardization: Different departments or trainers may use different criteria.
- Time and resource constraints: Designing effective assessments takes effort.
- Data silos: Learning data may not be integrated with performance or HR systems.
- Subjectivity in soft skills assessment: Measuring traits like leadership or empathy requires nuanced tools.
This is where intelligent learning platforms like Tekstac come into the picture.
How Tekstac Measures Learning Outcomes That Matter
Tekstac is a 360° skilling platform that integrates learning, assessments, and analytics to provide a holistic view of learner development. Unlike traditional LMS or LXPs, Tekstac is designed to focus on outcomes, not just activities. Its learning engine is built to simulate real-world scenarios and projects that mirror actual workplace challenges.
Tekstac assessments cover multiple formats, including auto-evaluated coding tasks, case-study evaluations, scenario-based MCQs, and AI-proctored video assessments. Each assessment is role-mapped, which ensures that learners are tested on job-relevant skills. This results in more precise measurement of learning outcomes and more actionable insights.
Driving ROI Through Outcome-Based Assessments with Tekstac
Tekstac’s assessment engine generates deep insights into skill proficiency, growth trajectory, and role readiness. For organizations, this means they can:
- Track individual and team-level learning outcomes in real time.
- Identify high-potential employees based on skill mastery.
- Close skill gaps by recommending targeted interventions.
- Align L&D initiatives with business objectives through data-backed decisions.
Ultimately, Tekstac doesn’t just help you assess what learners know- it helps you understand what they can do. And when learning outcomes are that clear, ROI follows naturally.
Ready to move from activity-based learning to outcome-based growth? Tekstac is your partner in building measurable, skill-focused learning ecosystems.
FAQs on Learning Outcome
1. What is the purpose of measuring learning outcomes?
Measuring learning outcomes helps organizations evaluate training effectiveness, identify skill gaps, and link learning to business results and ROI.
2. How do you measure learning outcomes in corporate training?
Through assessments, simulations, project-based evaluations, peer feedback, performance metrics, and AI-based learning analytics.
3. What is the difference between learning objectives and learning outcomes?
Learning objectives describe what training intends to teach; learning outcomes define what learners can actually do afterwards.
4. How do learning outcomes impact ROI?
They provide measurable evidence of performance improvement, enabling better budget allocation and business impact analysis.
5. Why is Learning Analytics important for L&D leaders?
Learning analytics enables L&D teams to demonstrate impact with measurable evidence, justify budget allocation, and optimize learning design based on real-world performance rather than assumptions.











