Why Content Chunking Is Key to Successful Upskilling and Reskilling Programs
January 30, 2025

Your employees are drowning.
Not in work, but in information.
Every training session feels like a firehose aimed straight at their heads—too much, too fast, and impossible to absorb.
Most organizations spend a fortune on upskilling and reskilling programs, yet only 30% of employees found the training ‘exceptionally rewarding.’
The problem isn’t the training itself; it’s how the information is served and how engaged employees feel. Overloaded minds don’t learn, they shut down. However, with content chunking, organizations can make every lesson stick and turn it into actual performance.
What is Content Chunking?
Content chunking is the process of breaking down information into smaller, bite-sized pieces that stick in the learner’s mind. It ensures learners focus on one concept at a time, reducing information overload and improving comprehension. When information is organized into logical sections, the learning is more effective, engaging, and memorable.
Example:
Imagine you’re creating a training on cybersecurity basics. Without chunking, it may look like this:
Cybersecurity refers to practices for protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. These include firewalls, anti-virus software, multi-factor authentication, data encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular software updates.
The above might take two or three takes before completely digesting it. Now, here’s the chunked version:
- What is cybersecurity? Protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber threats.
- Examples of protective measures are firewalls, anti-virus software, and multi-factor authentication.
- Why it matters: Safeguards sensitive data and prevents attacks.
The information is the same but easier to understand, retain, and apply. This reduces the time spent on repeated training sessions and keeps learners focused, thereby boosting the ROI of upskilling or reskilling programs.
How Content Chunking Enhances Upskilling and Reskilling Effectiveness?
By focusing on the “need-to-know” information, organizations can present it in accessible chunks, enabling learners to achieve better outcomes. Furthermore, content chunking increases the effectiveness of reskilling and upskilling programs in the following ways:
1. Prioritizes need-to-know information
Learners may face time constraints when upskilling and reskilling. Content chunking focuses on the most important information, eliminating irrelevant details. Core concepts are presented on screen with optional links for deeper information. For example, in a coding upskilling program, main syntax rules are displayed upfront, while examples and edge cases are accessible as hyperlinks.
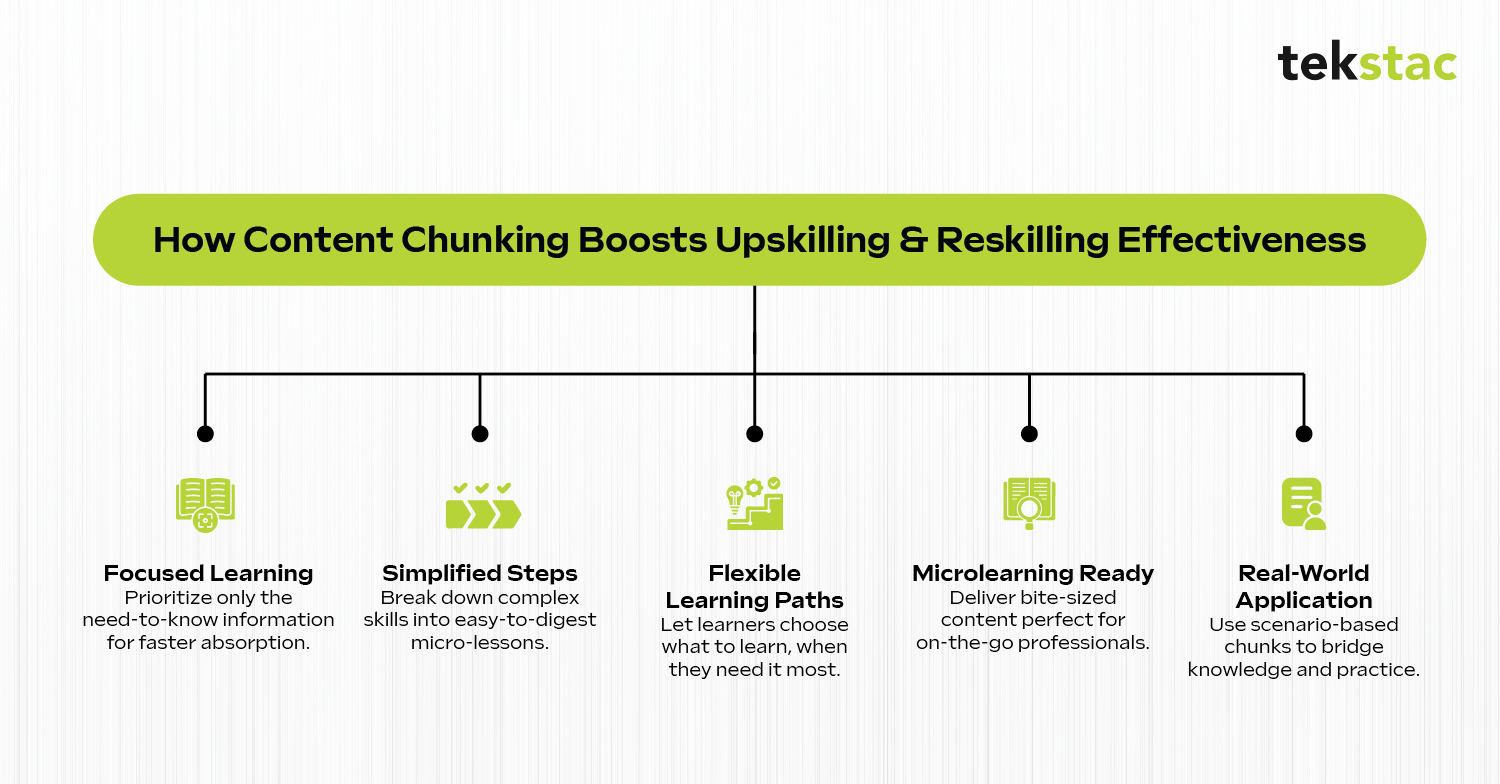
2. Simplifies new skills into manageable steps
It’s overwhelming when employees focus on a large skill set to learn within a stipulated time. Content chunking breaks learning tasks into micro-lessons, where employees can easily comprehend each chunk of content. For example, instead of delivering an entire module on “Advanced Data Analysis,” chunk the content into specific sections like “Introduction to Data Tools,” “Using Formulas Effectively,” and “Visualizing Data Insights”. Use clear progress indicators to guide learners step by step.
3. Facilitates modular learning paths
Chunked content creates modular learning experiences that can be consumed in any order. This allows learners to focus on the areas they need most, which is essential for personalized reskilling. For instance, a digital marketing reskilling program may have independent modules on SEO, content, PPC, and so on, allowing learners to start with their most immediate need.
4. Supports microlearning strategies
Microlearning delivers focused, short bites of learning ideal for busy professionals. Chunked content aligns perfectly with these approaches, ensuring each piece of information is highly targeted and digestible.
5. Enhances practical application through scenario-based microlessons
Reskilling often involves switching to unfamiliar roles or industries. Contextualized examples and learning methods make new skills more relatable and memorable. Such real-world scenarios help employees connect theory to practice. Imagine a learning reskilling for customer service. Content is chunked into micro-lessons like “Handling Difficult Customers,” “Using CRM Tools,” and “Upselling Techniques,” each with relevant, bite-sized simulations.
Different Ways of Content Chunking for Reskilling and Upskilling
Content chunking includes various methods to deliver practical learning experiences for reskilling and upskilling. Each method listed below caters to different learning styles, goals, and organizational needs.
1. Microlearning: Breaking content into small, standalone lessons
Here, topics are broken down into short, independent modules that learners can complete within 10 minutes. Each module focuses on a single concept, skill, or task. It aligns well with adults’ need for immediate relevance.
Example:
For upskilling in digital marketing, microlearning modules could include:
- Module 1: Introduction to SEO basics (5 minutes)
- Module 2: Keyword research tools and techniques (7 minutes)
- Module 3: Writing optimized meta descriptions (5 minutes)
2. Spaced learning: Distributing content over time
Spaced learning involves breaking up learning lessons with rest intervals or other activities. The main goal is to reinforce memory and retention. Spaced repetition combats the “forgetting curve” by revisiting main concepts periodically.
Example:
For upskilling in data analysis, you might:
- Teach basic data visualization today
- Review it with a quick quiz in three days
- Introduce advanced visualization tools the following week
3. Visual chunking: Using infographics or videos
Visual chunking involves presenting information using videos, infographics, or charts. It helps process information faster, especially for visual learners and helps present concepts better visually.
4. Task-based chunking: Organizing content around specific tasks
This is an approach where you break content into actionable tasks that can be performed as learners move through the content material. It ensures hands-on practice. For example, for upskilling in project management, organizations can chunk tasks as follows:
- Setting up a project timeline
- Assigning roles using project management software
- Monitoring task completion and generating reports
5. Layered chunking: Building knowledge gradually
Layered chunking introduces foundational concepts and adds difficult ones as learners gain proficiency. For reskilling, it bridges knowledge gaps, builds confidence with basics first and reduces overwhelm. Upskilling deepens expertise as the employee progresses through the learning material.
Rethink how you reskill and upskill your employees
With AI, organizations must rethink skilling. Traditional skilling methods may become slow, disconnected, and unprepared to meet the pace skills gap. Tekstac redefines upskilling and reskilling with its all-in-one SaaS-based skilling platform. It empowers businesses to create a skills-based organization through.






Insightful